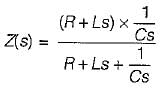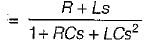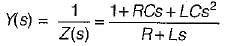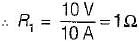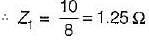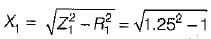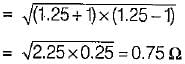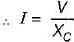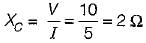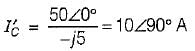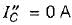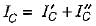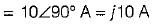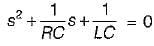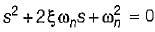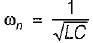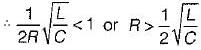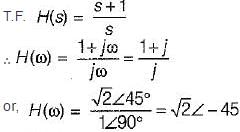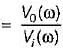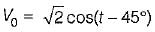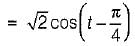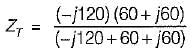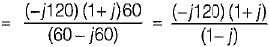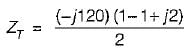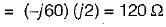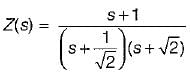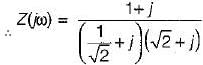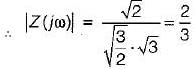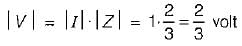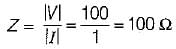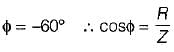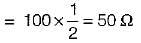Test: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis- 2 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis- 2
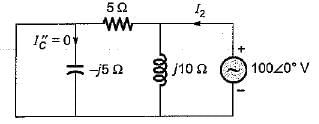
The driving point admittance of the network shown below is
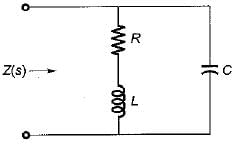

Figure shown below represents a d.c. 10 V voltage source as well as a 10 V a.c. 50 Hz voltage source while Z1 and Z2 are two unknown impedances. When Z1 is connected across 10V d.c. source, it draws a current of 10 A while it draws a current of 8 A if connected across 10V a.c. source.
Now, when Z2 is connected across 10 V d.c. source, it does not draw any current while it draws a current of 5 A if connected across 10 V a.c. source.
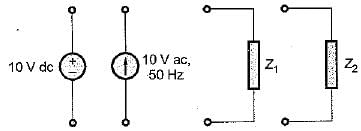
Q. What are the elements in Z1 and Z2?
Now, when Z2 is connected across 10 V d.c. source, it does not draw any current while it draws a current of 5 A if connected across 10 V a.c. source.

Q. What are the elements in Z1 and Z2?
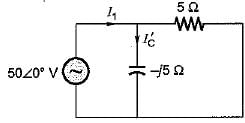
The current through the capacitor in the given circuit is

A parallel RLC circuit is said to be underdamped when
Assertion (A): A coil, when connected across 230 V dc supply, will draw more current in comparison to that when connected across 230 V ac supply.
Reason (R): The inductance of the coil opposes the flow of alternating current (not that of direct current).
A two terminal black box contains one of the R-L-C elements. When the black box is connected to a 220 V ac supply, the current through the source is I. When a capacitance of 0.1 F is inserted in series between the source and the box, the current through the source is 2I. The element is
A system function has a pole at s = 0 and zero at s = -1. The constant multiplier is unity. For an excitation cost, the steady state response is given by
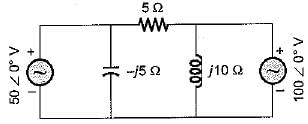
For the a.c. circuit given below, what is the value of I?
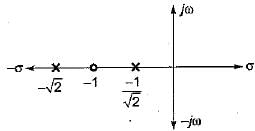
Consider the following pole-zero diagram of a system,
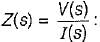
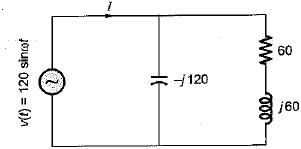
What will be the magnitude of the voltage phasor for i(t) = sint?
A coil takes a current of 1∠60° A (lag) from a 100 V, 50 Hz supply. The resistance of the coil is