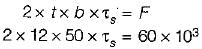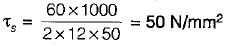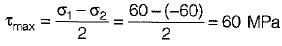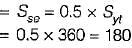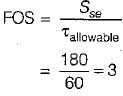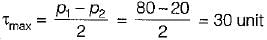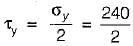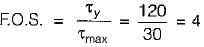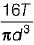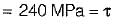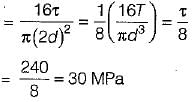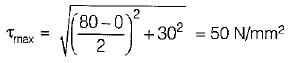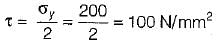Test: Design Against Static Load - 3 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Design Against Static Load - 3
A cotter joint is used when no relative motion is permitted between the rods joined by the cotter. It is capable of transmitting
Which of the following joint is commonly used for pipes carrying water at low pressure
In a gib and cotter joint, the gib and cotter are subjected to
In a cotter joint the width of the cotter at the centre is 50 mm and its thickness is 12 mm. The load acting on the cotter is 60 kN. What is the shearing stress developed in the cotter?
Match List-I (Application) with List-ll (Joint) and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List-I
A. Boiler Shell
B. Marine Shaft Coupling
C. Crosshead and Piston Rod
D. Automobile gear box (gears to shaft)
List-II
1. Cotter Joint
2. Knuckle Joi
3. Riveted join
4. Splines
5. Bolted Joint
Codes:
A B C D
(a) 1 4 2 5
(b) 3 5 1 4
(c) 1 5 2 4
(d) 3 4 1 5
A cold rolled steel shaft is designed on the basis of maximum shear stress theory. The principal stresses induced at its critical section are 60 MPa and -60 MPa respectively. If the yield stress for the shaft material is 360 MPa, the factor of safety of the design is:
A thin cylindrical tube closed at ends is subjected to internal pressure. A torque is also applied to the tube. The principal stresses p1 and p2 developed are 80 unit and 20 unit respectively. If the yield stress is 240 units then what is the factor of safety according to maximum shear stress theory
Maximum shear stress developed on the surface of a solid circular shaft under pure torsion is 240 MPa. If the shaft diameteris doubled, then what is the maximum shear stress developed corresponding to the same torque?
A shaft is subjected to maximum bending moment of 80 N/mm2 and a maximum shear stress equal to 30 N/mm2 at a particular section. If the yield point in tension of the material is 200 N/mm2 and maximum shear stress theory is used, the FOS will be
A cotter joint is used when no relative motion is permitted between the rods joined by the cotter. It is capable of transmitting