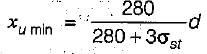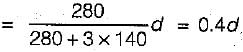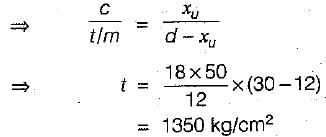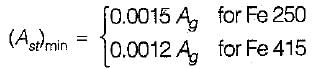Test: Beams & Slabs - 3 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Beams & Slabs - 3
A reinforced concrete member is subjected to combined action of compressive axial force and bending moment. If εc is the least compressive strain in the member, fy, the yield stress of steel and, Es, the modulus of elasticity of steel, the maximum permissible compressive strain in concrete member will be
The span to depth ratio limit is specified in IS: 456-2000 for the reinforced concrete beams, in order to ensure that the
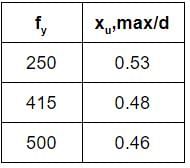
As per the provisions of IS : 456-2000, in the limit state method for design of beams, the limiting value of the depth of neutral axis in a reinforced concrete beam of effective depth 'd' is given as
If the permissible stress in steel in tension is 140 N/mm2, then the depth of neutral balanced section using working stress method is
A continuous beam is deemed to be a deep beam when the ratio of effective span to overall depth (l/D) is less than
According to IS 456 recommendations,'the maximum depth of stress block for balanced section of a beam of effective depth d is
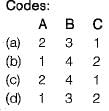
For a continuous R.C. beam, match List-I (Condition) with List-II (Placement of live load) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists.
List-I
A. For maximum sagging moment in a span
B. For maximum hogging moment at a support
C. For maximum hogging moment in a span
List-II
1. The span adjoining the span as well as alternate span
2. The same span as well as alternate spans
3. The adjacent spans on both sides of this support as well as spans alternate to these
4. Spans next to the adjacent spans of the support plus alternate spans
In a doubly reinforced rectangular beam, the allowable stress in compression steel is
The side face reinforcement, if required, in a 7-beam’will be
The effective depth of a singly reinforced rectangular beam is 30 cm. The section is over reinforced and the neutral axis is 12 cm below the top. If the maximum stress attained by- concrete is 50 kg/cm2 and the modular ratio is 18, then the stress developed in steel would be
Which one of the following statements about the percentage of tensile steel required to produce a balanced reinforced concrete section is correct?
The required percentage of steel
Minimum clear cover (in mm) to the main steel bars in slab, beam, column and footing respectively are
Beam sections designed in accordance with LSM as compared to sections designed in accordance with WSM will have
If the depth of actual neutral axis in a beam is more than the depth of critical neutral axis, the beam is called:
For a continuous slab of 3 m x 3.5 m size the minimum overall depth of slab to satisfy vertical deflection limits is
The minimum reinforcement using mild steei in slab should not be less than
In the reinforced concrete slab, the spacing between main reinforcement should not exceed
The reinforced concrete beam curved in plane is designed for