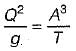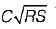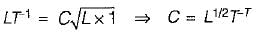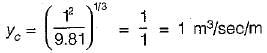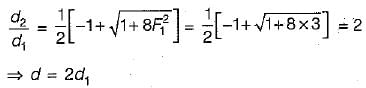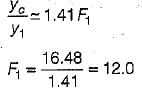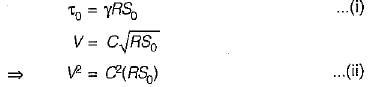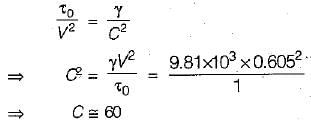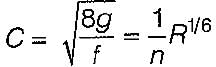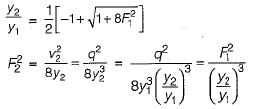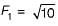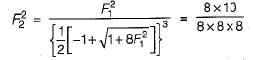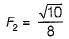Test: Flow Through Open Channels - 3 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Flow Through Open Channels - 3
Which of the following conditions are applicable for critical flow
The Chezy’s constant C in the Chezy’s equation for mean velocity in open channels is
The conveyance K of a channel is a measure of its carrying capacity. In terms of K, the discharge Q is given by
A steady discharge of 1 cumec flows uniformly in a rectangular channel 1 m wide at a depth of 250 mm. The slope of the channel bed is
In case of a hydraulic jump in a rectangular channel, the post jump, depth d2, when Froude number F1 is √3 , is
where d1 = pre-jump depth
The flow characteristic before and after a hydraulic jump are such that:
The figure below shows a gradually varied flow situation in an open channel with a break in bed slope. Types of water surface profiles occurring from left to right are

The sequent depth ratio in a. hydraulic jump formed in a horizontal rectangular channel is 16.48. The Froude number of the supercritical stream is
An open channel carries water with a velocity of 0.605 m/s. If the average bed shear stress is 1.0 N/m2, then the Chezy’s constant C is equal to
The Chezy’s and Manning’s formulae are related by
In a subdritica! flow, as the specific energy in a channel is decreased, the depth of flow
If the specific energy at the upstream section of a rectangular channel is 3 m and minimum specific energy is 2.5 m, the maximum height of jump without causing afflux will be
If the Froude’s number before a hydraulic jump occurring in a rectangular horizontal channel is √10 then the Froude’s number after the jump will be
Least possible value of correction factor for
1. kinetic energy is zero
2. kinetic energy is 1
3. momentum is zero
4. momentum is 1
The correct statements are
If velocity is zero over 1/3rd of a cross-section and is uniform over remaining 2/3rd of the cross- section, then the correction factor for kinetic energy is
The depth of flow for maximum velocity in a circular channel section with diameter equal to 1.5 m is
The critical depth of flow in a most economical triangular channel section for a discharge of 1 m3/sec is given by
Gradually varied flow in open channel is caused when