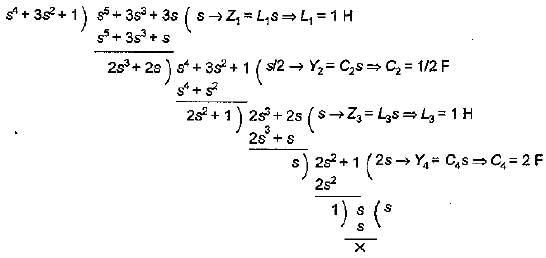Test: Network Synthesis- 2 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Network Synthesis- 2
The driving point admittance of the network shown below is
Which of the following is a PRF (positive real function)?
A function F(s) is defined as
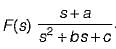
The necessary condition required for F(s) to be a positive real function is
What is the range of values of m in P(s), so that P(s) is a Hurwitz polynomial?
P(s) = (2s4 + s3 + ms2 + s + 2)
Consider the impedance functions:
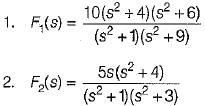
Out of the above impedance function which are driving point LC immittances of LC network?
Cauer and Foster forms of realizations are used only for
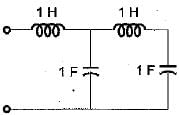
The driving point impedance function
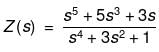
can be realized as
Match List - I (Network functions) with List - II (Type of functions) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List - I
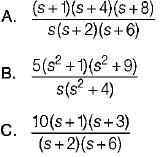
List - II
1. LC immittance function
2. RC admittance function
3. RL admittance function
4. RLC network function
Codes:
Assertion (A): Foster’s type - I and Foster’s type - II networks are equivalent networks.
Reason (R): Foster’s type - I and Foster’s type - II networks are dual of each other.
Assertion (A): The realization of one port LC networks can be done in two. configurations (commonly known as Cauer-I and Cauer-II forms) using the continued fraction expansion of the driving point impedance.
Reason (R): The basic form of the Cauer realization being a ladder type network.



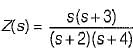 represent a
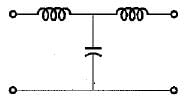
represent a 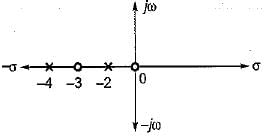
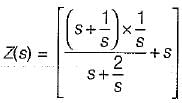
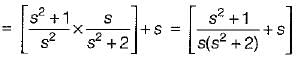
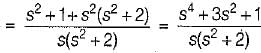
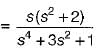
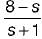 is not a PRF since all the coefficients of numerator polynomial are not positive and there is a zero in RH s-plane.
is not a PRF since all the coefficients of numerator polynomial are not positive and there is a zero in RH s-plane.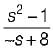 is not a PRF due to the same reason (zeros are at s = ± 1).
is not a PRF due to the same reason (zeros are at s = ± 1).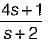 is a PRF since pole is at s =
is a PRF since pole is at s = 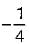 and zero at s = - 2 .
and zero at s = - 2 .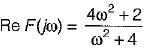 and
and 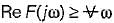
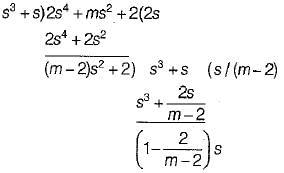
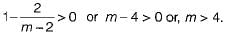
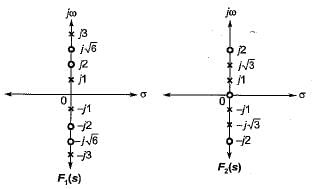
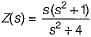 is not realizable because the
is not realizable because the