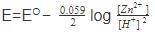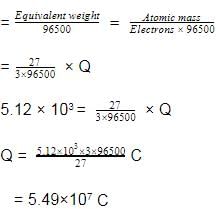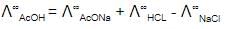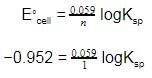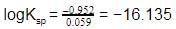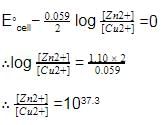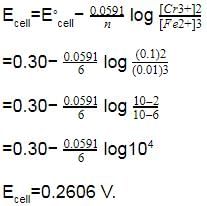Test: JEE Previous Year Questions- Electrochemistry - JEE MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test - Test: JEE Previous Year Questions- Electrochemistry
For the following cell with hydrogen electrodes at two different pressure p1 and p2
Pt(H2)|H+ (aq.)|Pt(H2)| H+ (aq.) emf is given by – p1 p2
[AIEEE-2002]
Which of the following reactions is possible at anode ?
[AIEEE-2002]
For a cell given below Ag | Ag+ || Cu2+ | Cu
— +
Ag+ + e- → Ag, Eº = x
Cu2+ +2e- → Cu, Eº = y
Eº cell is –
[AIEEE-2002]
For a cell reaction involving a two-electron change the standard e.m.f. of the cell is found to be 0.295 V at 25ºC. The equilibrium constant of the reaction at 25º C will be –
[AIEEE-2003]
Standard reduction electrode potentials of three metals A, B and C are respectively +0.5 V, – 3.0V and – 1.2 V. The reducing powers of these metals are -
[AIEEE-2003]
For the redox reaction :
Zn (s) + Cu2+ (0.1M) → Zn2+ (1M) + Cu(s) taking place in a cell, Eºcell is 1.10 volt. Ecell for the cell will be
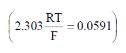
[AIEEE-2003]
When during electrolysis of a solution of AgNO3 9650 coulombs of charge pass through the electroplating bath, the mass of silver deposited on the cathode will be –
[AIEEE-2003]
Consider the following E° values
[AIEEE-2004]
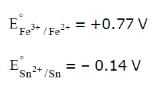
under standard conditions the potential for the reaction
Sn(s) + 2Fe3+ (aq) → 2Fe2+ (aq) + Sn2+ (aq) is
The standard e.m.f. of a cell, involving one electron change is found to be 0.591 V at 25°C. The equilibrium constant of the reaction is (F = 96500 C mol-1 ; R = 8.314 JK-1mol-1)
[AIEEE-2004]
The limiting molar conductivities ^° for NaCl, KBr and KCl are 126, 152 and 150 S cm2 mol-1 respectively. The ^° for NaBr is –
[AIEEE-2004]
In a cell that utilises the reaction
Zn(s) + 2H+ (aq) Zn2+ (aq) + H2(g)
addition of H2SO4 to cathode compartment, will–
[AIEEE-2004]
Aluminium oxide may be electrolysed at 1000ºC to furnish aluminium metal (At. Mass=27 amu ; 1 Faraday = 96,500 Coulombs). The cathode reaction is
Al3+ + 3e-→ Alº
To prepare 5.12 kg of aluminium metal by this method would require -
[AIEEE-2005]

Calculate using appropriate molar conductance of the electrolytes listed above at infinite dilution in H2O at 25ºC
[AIEEE-2005]
For a spontaneous reaction the ΔG, equilibrium constant (K) and Ecell will be respectively -
[AIEEE-2005]
Given the data at 25ºC,
Ag + I- → AgI + e- Eº = 0.152 V
Ag → Ag+ + e- Eº = -0.800 V
What is the value of log Ksp for AgI ?
(2.303 RT/F = 0.059 V)
[AIEEE 2006]
The cell, Zn | Zn2+ (1M) | | Cu2+(1M)|Cu (Eºcell)=1.10 V), was allowed to be completely discharged at 298 K.
the relative concentration of zn2+ to 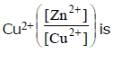
The equivalent conductance of two strong electrolytes at infinite dilution in H2O (where ions move freely through a solution) at 25ºC are given below -
^°CH3COONa= 91.0 S cm2/equiv
^ºHCl = 426.2 S cm2/equiv
What additional information/quantity one needs to calculate Lº of an aqueous solution of acetic acid ?
[AIEEE 2007]
Given EºCr3+/Cr = – 0.72 V, EºFe2+/Fe= – 0.42 V. The potential for the cell Cr |Cr3+ (0.1 M)| |Fe2+ (0.01 M) | Fe is -
[AIEEE 2008]
The standard reduction potentials for Zn2+/Zn, Ni2+ /Ni, and Fe2+/Fe are – 0.76, – 0.23 and – 0.44 V respectively. The reaction X + Y2+ → X2+ + Y will be spontaneous when –
[AIEEE 2012]
Given
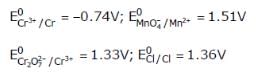
Based on the data given above, strongest oxidisting agent will be
[AIEEE 2013]
Refining of impure copper with zinc impurity is to be done by electrolysis using electrods as –
[AIEEE-2002]