Laxmikanth Test: Making of the Constitution- 3 - Super TET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Laxmikanth Test: Making of the Constitution- 3
Consider the following statements:
I. The Interim Government of India formed the Constituent Assembly in 1946.
II. The Muslim League did not participate in the formation of the Interim Government.
III. In 1946, only 296 seats in the Constituent Assembly were open for assigned to the British Indian provinces.
Choose the statements which is true :
I. The Interim Government of India formed the Constituent Assembly in 1946.
II. The Muslim League did not participate in the formation of the Interim Government.
III. In 1946, only 296 seats in the Constituent Assembly were open for assigned to the British Indian provinces.
Choose the statements which is true :
Consider the following statements:
1. It was M. N Roy who first proposed the idea of forming a Constituent Assembly through universal adult suffrage.
2. The demand was accepted by the British for the first time in the Cripps’ Mission.
Choose the correct answer:
1. It was M. N Roy who first proposed the idea of forming a Constituent Assembly through universal adult suffrage.
2. The demand was accepted by the British for the first time in the Cripps’ Mission.
Choose the correct answer:
Consider the following table and find the wrong matches:
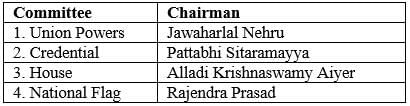

Arrange the following events in their correct chronological order:
1. Ratification of India’s membership of the Commonwealth
2. Adoption of National Flag
3. Adoption of National Anthem
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Consider the following provisions of the Constitution of India:
1. Citizenship
2. Electoral Process in India
3. Fundamental Duties
4. Fundamental Rights
5. Formation of States and Union Territories
Which of the above provisions came into existence on November 26, 1949?
Consider the following statements:
1. There were 13 major committees that were formed to draft the Constitution.
2. N. Madhav Rau was a member of the Drafting Committee.
3. Sarojini Naidu was the only woman to head a Committee.
Select the correct answer:
Consider the following statements:
1. With the adoption of the Constitution in 26 November 1949, the Government of India Act, 1935 ceased to exist.
2. The Constitution as of 26 November 1949 contained only 8 Schedules.
Choose the incorrect statement(s):
The provisions relating to emergency have been adopted from which of the following:
I. Government of India Act, 1935
II. Irish Constitution
III. Weimar Constitution
IV. South African Constitution.
Choose the correct statement(s):
Which one of the following is not a feature of the Government of India Act of 1935?
Which of the following communities had special representation in Constituent Assembly?
1. Muslims
2. Christians
3. Parsis
4. Sikhs
Choose the right option:
The Constituent Assembly was formed during the rule of:
Given below are two statements, one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other as Reason (R):
Assertion (A): Constituent Assembly was not a representative body as its members were not elected based on universal adult franchise.
Reason (R): Constituent Assembly was created against the proposal of the British government.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
The constituent assembly was constituted under the scheme formulated by the Cabinet Mission Plan. Regarding the plan consider the following statements:
1. Allocation of seats for each province and princely state to be in proportion to their respective population
2. Representatives to be elected through proportional representation using a single transferable vote.
3. The representatives of the princely state were to be nominated by the heads of princely states.
4. Out of 296 seats allotted to British India, 291 members were to be drawn from the governor’s provinces and 5 from the chief commissioners’ provinces.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. January 26 was specifically chosen as the ‘date of commencement’ of the Constitution because on this day in 1930 that Poorna Swaraj day was celebrated.
2. With the commencement of the Constitution, the Indian Independence Act of 1947 and the Abolition of Privy Council Jurisdiction Act (1949) was repealed.
Which of the following statements above is/are not correct?
Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Indian Constitution?
1. The original constitution of India was handwritten by Prem Behari Narain Raizada.
2. It was written in a flowing italic style.
3. The calligraphy of the Hindi version of the original constitution was done by Vasant Krishan Vaidya.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:














