Test: Matter In Our Surroundings (Medium) - Class 9 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Matter In Our Surroundings (Medium)
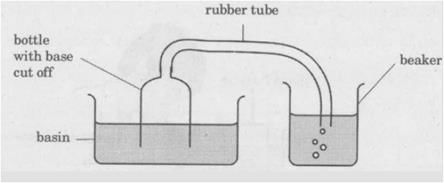
Meena experimented, as shown below. When she pushed the bottle into the basin of water, she could see bubbles escaping from the rubber tube into the beaker of water. What can she infer from her Experiment?

With Increase Of Temperature, which of these changes
Which of the following is not the characteristic for the matter?
Water stored in earthen pots become cool in summer because:
Which of the following information regarding the tube is correct?
On Increasing Temperature, the rate of diffusion
Venu blows into the straw, as shown above. What will be observed?
Which of the following is a surface phenomenon?
During summer water kept in an earthen pot becomes cool because of the phenomena of
Which of the following conditions will increase the evaporation of water?
When a burner supplies heat to boiling water, then the temperature of the water during vaporization
A liquid boils at 100°C. Its temperature can also be expressed as
The three states of water; ice, water and steam can be arranged in the decreasing order of interparticle forces as
When water solidifies to ice, then heat is
Which of the following states has maximum energy?














