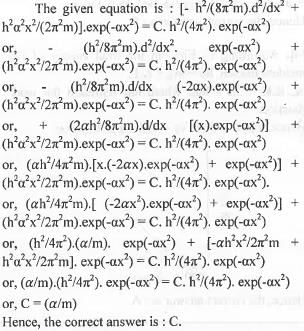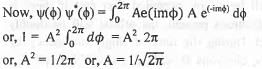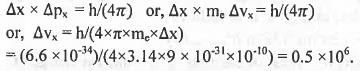Test: Atomic Structure - IIT JAM MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Atomic Structure
Wave nature of electromagnetic radiation is observed in
1. Diffraction ;
2. Interference ;
3. Photoelectric effect ;
4. Compton scattering.
[2017]
Ionization energy of hydrogen atom in ground state is 13.6 eV. The energy released (in eV) for the third member of Balmer series is
[2017]
The 3pz orbital
1. one radial node ;
2. two radial nodes ;
3. one angular node ;
4. two angular nodes.
[2016]
The ground state term for a free ion with 3d7 configuration is
[2015]
[- h2/(8π2m).d2/dx2 + h2α2x2/(2π2m)].exp(-αx2) = C. h2/(4π2). exp(-αx2), where h, π, m and α are constant. Then C is
[2014]
The energy of an electron in a hydrogenic atom with nuclear charge Z varies as :
[2014]
Identify the correct statement regarding Einstein s photoelectric effect
1. The no. of electrons ejected depends on the wavelength of the incident radiation.
2. Electrons ejection can occur at any wavelength of incident radiation.
3. The no. of electrons ejected at a given incident wavelength depends on the intensity of the radiation.
4. The kinetic energy of the ejected electrons is independent of the wavelength of the incident radiation.
[2011]
If ψ is the eigen function to the Hamiltonian operator with a as the eigen value, then α must be
[2010]
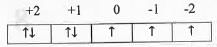
The acceptable valence shell electronic arrangement is :
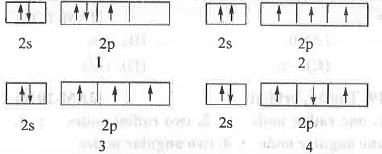
[2019]
An electron is found in an orbital with an orbital node and two angular nodes. Which orbital the electron is in?
[2009]
For a particle in a cubical box, the total number of quantum no. needed to specify its state are
If the electrons were spin 3/2 particles, instead of spin 1/2, then the no. of electrons that can be accommodated in a level are
[2008]
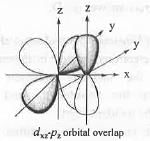
The overlap between the atomic orbitals sketched is
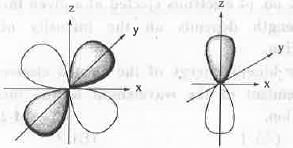
[2007]
The normalization constant A for the wave function ψ(φ) = Ae(imφ) where 0 ≤ φ ≤ 2π is
[2007]
Which one of the following species is not isoelectronic with CO?
[2007]
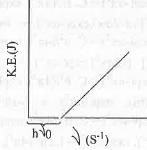
Which of the following figures, showing K.E. of the ejected electron vs. the frequency (v) of the incident photon, represents the Einstein's photoelectric effect?
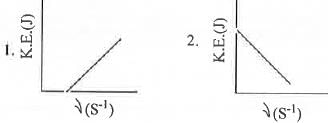
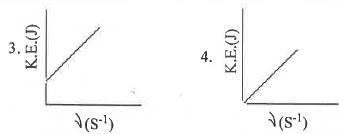
[2007]
The wave function for a particle (moving in a ring) is (2π)-1/2 exp(2iφ) , where φ is the polar angle. The probability of finding the particle in a small interval dφ when the value of φ = π/2 is
[2006]
For an electron whose x-positional uncertainty is 10~10 m and the uncertainty in the x-component of the velocity in ms-1 will be in the order of (Data : me = 9 x 10-31 kg, h = 6.6 x 10-34Js)
For H-like atoms, the ground state energy is proportional to