Test: Reproduction in Organisms - 3 (Old NCERT) - Grade 12 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Reproduction in Organisms - 3 (Old NCERT)
Reproduction is essential for living organisms in order to
A chain of yeast cells forms because
__ type of reproduction takes place in Hydra.
Assertion: The endometrium undergoes cyclical changes during menstrual cycle.
Reason: The myometrium exhibits strong contractions during delivery of the baby.
Assertion: All members of bee society are diploid except the drones.
Reason: Drones are produced parthenogenetically.
A student after observing a slide showing different stages of binary fission in Amoeba draws the following diagrams.
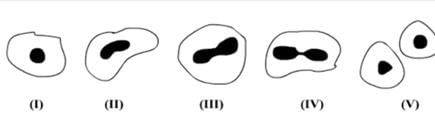
However, These diagrams are not in proper sequence:
The correct sequence is:
During the fourth and sixth cleavage of the zygote
A potato tuber is sown in a pot and pot is placed in the freezer of refrigerator. New plants will:
Which of the following does not take place during the final stage of the menstrual cycle?
I Further thickening of the uterine lining
II Repair and growth of the uterine lining
III Ovulation
Which one of the following is correct?
Amoeba is most commonly reproduced by:
Which of the following is correct?
Pollination is a characteristic of














