Test: Reproduction in Organisms - 4 (Old NCERT) - CUET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Reproduction in Organisms - 4 (Old NCERT)
A piece of potato tuber will form a new plant if it has
Oogamous sexual reproduction involves fusion of
In oogamy,fertilization occurs between
Budding, in hydra, is a form ________
Repair of endometrium is undertaken by
__________ refers to an asexual reproduction process wherein genetically identical copies of individual plants are produced
In an examination Raj drew diagrams of four stages of binary fission in Amoeba as shown below.
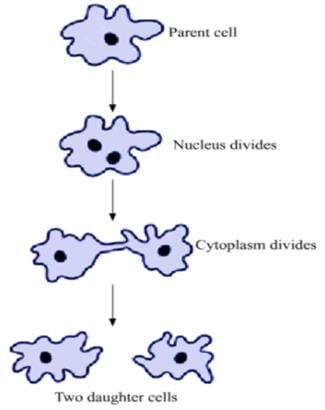
However, he was not awarded full marks as one of the stages was incorrectly drawn. The incorrectly drawn stage is:
Sexual spores produced by Penicillium
In binary fission, the parent cell divides by the process:
The fusion of gametes is called as
Animals which give birth to young ones are called as
The development of root and shoot in tissue culture is determined by ______
The term scion is used in relation to :
The reproduction takes place by gemma :
Vegetative reproduction takes place in Bryophyllum :
The phenomenon observed in some plants where in parts of the sexual apparatus is used for forming embryos without fertilisation is called.



















