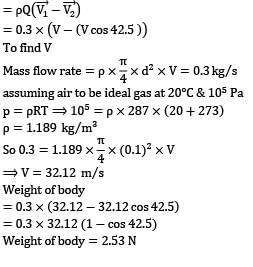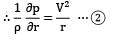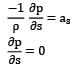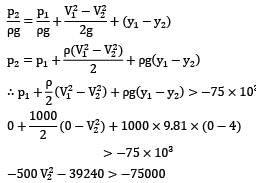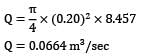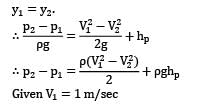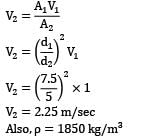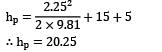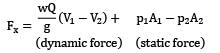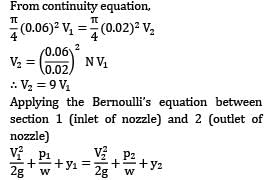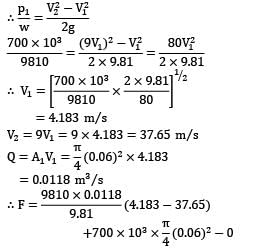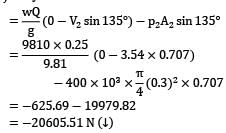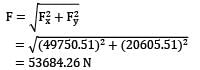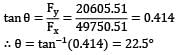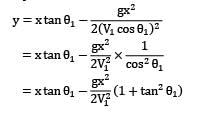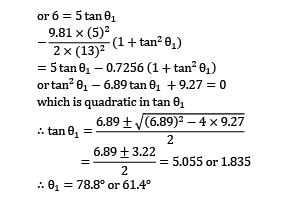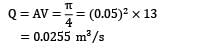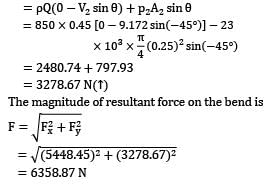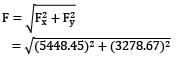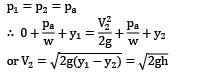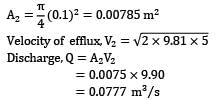Test: Fluid Dynamics Level - 3 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Fluid Dynamics Level - 3
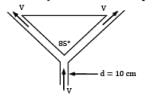
Air at 20°C and 105 Pa enters the bottom of an 85° conical flow meter duct at a mass flow rate of 0.3 kg⁄s, as shown in the figure. It supports the centered conical body by steady annular flow around the cone and exits at the same velocity as it enters. Estimate the weight of the body in Newton’s

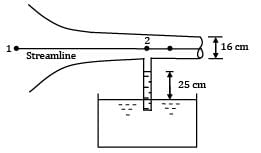
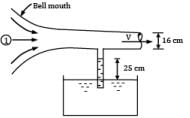
An air compressor draws air from the atmosphere through a bell-mouth entrance calibrated for measuring discharge passing through it in terms of height of water that rises in a single tube manometer installed in the duct which takes air from the bell mouth to the compressor. Determine the flowrate of air through the bell-mouth if the rise of water in the manometer tube is 25 cm and the duct has a diameter of 16 cm. For air density ρ = 1.2 kg⁄m3.
Refer Fig. for the set-up.

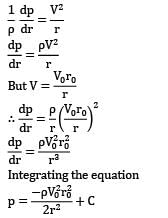
Consider a flow field given by circular streamlines. The velocity field for the flow is as follows.
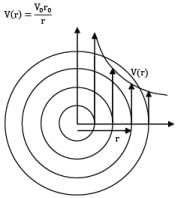
Predict the pressure distribution p(r) in the flow.
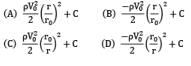

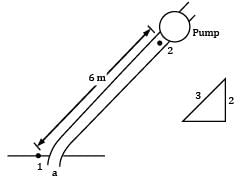
The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 along the pipe, which is 10 cm in diameter. The pipe is 6 m long; its lower end being just below the surface of water in the reservoir. For design reasons, it is undesirable that pressure at inlet to the pump fall more than 75 kN⁄m2 below atmospheric pressure. Neglecting friction, make calculations for the maximum discharge (in L/s) that the pump may deliver.
Take atmospheric pressure = 100 kN⁄m2
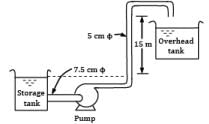
In the equipment shown in Fig., a pump draws a solution (specific gravity 1.85) from a store tank through a 7.5 cm steel pipe in which the flow velocity is 1.0 m⁄s . The pump discharges through a 5 cm steel pipe to an overhead tank, the end of the discharge pipe is 15 m above the level of the solution in the feed tank, and the friction losses in the entire piping system are 5 m. What is the pressure difference in (in kPa) maintained across the pump? Take pump efficiency as 60 percent.
A fireman holds a water hose ending into a nozzle that issues a 20 mm diameter jet of water. If the pressure of water in the 60 mm diameter hose is 700 kPa, find the force (in N) experienced by the fireman.
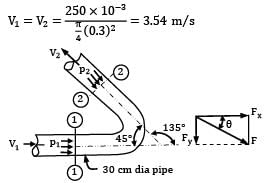
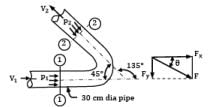
Water is flowing at a rate of 250 lt/sec. through a pipe of 30 cm diameter. If the pipe is bent by 135°, find the magnitude and direction of resultant force on the bend. The pressure of water flowing in the pipe is 400 kPa.
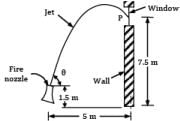
A fire-brigade man is holding a fire stream nozzle of 5 cm diameter as shown in Fig. The jet issues out with a velocity 13 m/s and strikes the window. Find the angle or angles of inclination with which the jet issues from the nozzle. What will be the amount of water falling on the window?
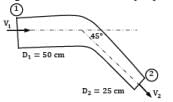
A pipe bend placed in a horizontal plane tapers from 50 cm diameter at inlet to 25 cm diameter at outlet. An oil of density 850 kg⁄m3 enters the reducing bend horizontally and gets turned through 45° clockwise direction. Measurements indicate that when oil flows at the rate of 0.45 m3⁄s, the pressure of 40 kN⁄m2 at the inlet section drops to 23 kN⁄m2 at the outlet section due to frictional effects. Make calculations for the magnitude of force on the bend. (in N)
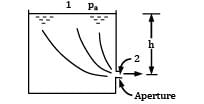
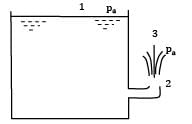
Water flows from a large tank, open to the atmosphere, through a 10 cm diameter well rounded aperture in its side. The free surface of water is 5 m above the centerline of the aperture. Calculate the velocity of jet issuing from the hole and the discharge. If a 90° elbow is placed at exit from the aperture, determine how high the water will reach.