Test: Design of Bearings Level - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Design of Bearings Level - 2
The most suitable bearing for carrying very heavy loads with slow speed is
Match List-I (Type of Bearings) with List-II (Type of Load) and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists.



A ball bearing is characterized by basic static capacity = 11000 N & dynamic capacity = 18000 N. This bearing is subjected to equivalent static load =5500 N . The bearing loading ratio and life in million revolutions respectively are
Which one of the following is correct?
A hydrodynamic slider bearing develops load bearing capacity mainly because of
A full journal bearing having clearance to radius ratio of 1/100, using a lubricant with μ = 22 X 10-3 as supports the shaft journal running at N = 2400 r.p.m. If the bearing pressure is 1.4 MPa, the Sommerfeld’s number is
What is the main advantage of hydrodynamic bearing over roller bearing?
Match List-I (Type of Anti-friction bearing) with List-II (Specific Use) and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists:

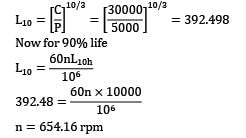
A roller bearing has a dynamic load capacity of 30 kN and radial load acting on bearing is 5 kN. The desired life for 90% of the bearing is 10000 hr. What is the speed (in rpm) at which bearing is working?
A full journal bearing have clearance to radius ratio of 1/200. The lubricant with μ = 40 X 10-3 Pa-s supports the shaft journal running at 3000 rpm. If the bearing pressure is 1.5 MPa, the Sommerfeld’s number is
To restore stable operating condition in a hydrodynamic journal bearing, when it encounters higher magnitude loads,
A 6308 bearing rotating at 800 rpm is subjected to a dynamic load of 20500 N. The static and dynamic load ratings are 22400 N and 41000 N respectively. The life of bearing in hours is Options~
(A) 124.4
(B) 166.7
(C) 182.3
(D) 144.3
A journal bearing of diameter 25 cm and length 40 cm carries a load of 150 kN. The average bearing pressure is
A ball bearing operating at a load P has 16000 hours of life. The life of the bearing, in hours, when the load is doubled to 2P is
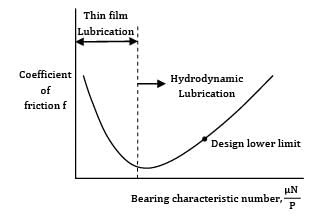
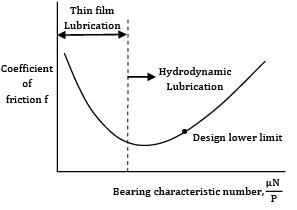
In thick film hydrodynamic journal bearings, the coefficient of friction
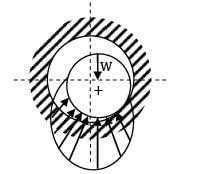
Assertion (A): In steady rotating condition the journal inside a hydrodynamic journal bearing remains floating on the oil film.
Reason (R): The hydrodynamic pressure developed in steady rotating conditions in journal bearings balances the load on the journal
The following data is given for a hydrodynamic bearing:
Radial load = 12kN
Journal speed 1500rpm
Clearance ratio = 850
viscosity = 35centipoise
Journal diameter = 100 mm
Assuming a square journal bearing, the Sommerfeld’s number is
A shaft of 120 mm diameter rotates at 100 rpm in a 200 mm long bearing. The angular space between the shaft and bearing is filled with oil of viscosity 0.7 poise. If the thickness of oil film is 0.075 mm, the power absorbed in the bearing is __________ W.
A taper roller bearing has a dynamic load capacity of 26 kN. The desired life for 90% of the bearings is 8000h and the speed is 300 rpm. The equivalent radial load that the bearing can carry in N is
A journal bearing has journal diameter 50 mm and a bush length of 50 mm. The shaft is rotating at 250 rpm and viscosity of lubricant is 0.4 poise. The power loss (in W) will be __________. (Take clearance = 0.02 mm)
If load of a ball bearing is decreased from 12kN to 7.25 kN, life of the ball bearing will increased by __________ times.
A roller bearing dynamic load capacity of 30kN. Equivalent radial load that bearing can carry is 6 kN. The speed is 400 rpm. The desired life for 90% of bearings is __________ hours.
A full journal square bearing with journal of 100 mm diameter is subjected to a load of 5 kN at 1000 rpm. The lubricant has a viscosity of 12 centipoise, radial clearance is 0.04 mm and eccentricity ratio of the bearing is 0.27. The value of minimum oil thickness is __________ mm. (upto three digits)
The following data refers to a 360०hydrodynamic bearing:
Radial load = 3.0 kN.
Journal speed = 1500 r m
Journal diameter = 70 mm
Bearing Length = 100 mm
Radial clearance = 0.05 mm
Lubricant viscosity = 30 centipoise
The Sommerfeld’s number for the bearing is __________.
A deep groove ball bearing has a dynamic load capacity of 40000 N. Work cycle consists of 5000 N at 1440 rpm for 20% time, 3000 N at 2880 rpm for 50% time and 6000 N at 720 rpm for 30% time. The life of bearing is __________. (in million rev)
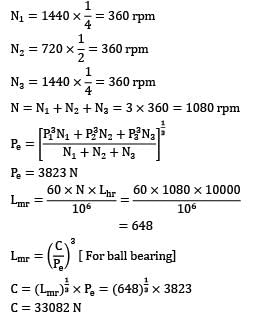
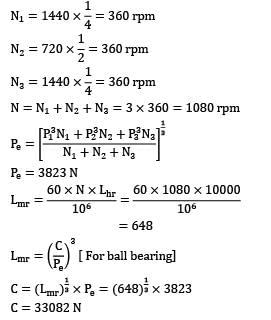
A ball bearing is operated on a work cycle consisting of three parts: a radial load of at 1440 rpm for one quarter cycle, a radial load of 5000 N at 720 rpm for one half of cycle and a radial load of 2500 N at 1440 rpm for the remaining cycle. The expected life of the bearings is 10, 000 hrs. The dynamic load carrying capacity of the bearings is
A bearing of 50 mm in diameter has a shaft speed of 320 rpm and a lubricating oil of viscosity 0.06 kg/m.s. The diametral clearance is 0.15 mm and the bearing pressure is 1.5 N/mm2 . If it is designed for a speed of 320 rpm and pressure of 1.5 N/2mm . Clearance of 0.12 mm, the change made for the viscosity is (in kg/m.s) is __________.
A 25 mm radius and 300 mm long shaft is supported at the ends by two journal bearings. A load of 2 kN acts on the shaft at a distance of 200 mm from the left bearing. The length to diameter ratio for the bearings is 1.5. The maximum bearings pressure induced is
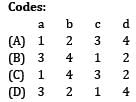
A system involves four identical ball bearings, each subjected to a radial load of 2500 N. The reliability of the system, i.e., one out of four bearings failing during the lifetime of five million revolutions, is 82%. The dynamic load carrying capacity of the bearing, so as to select it from the manufacturer’s catalogue based on 90% reliability will be



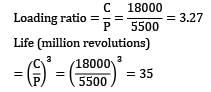
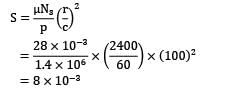
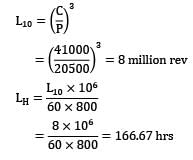
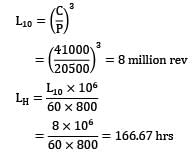


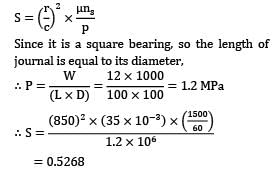


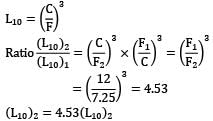


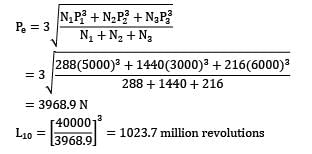


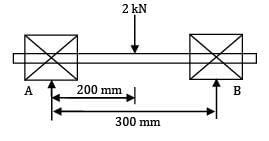
 MA = 0
MA = 0  RB x 300 = 2 x 200
RB x 300 = 2 x 200