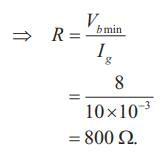Test: Basics and Power Semiconductor Devices - 1 - GATE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Basics and Power Semiconductor Devices - 1
Figure shows four electronic switches (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv). Which of the switches can block voltages of either polarity (applied between terminals a and b) when the active device is in the OFF state?
a a a a
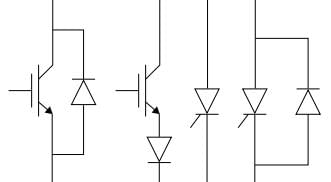
b b b b

The MOSFET switch in its on-state may be considered equivalent to
The typical ratio of latching current to holding current in a 20 A thyristor is
Circuit turn-off time of an SCR is defined as the time
Figure shows a composite switch consisting of a power transistor (BJT) in series with a diode. Assume that the transistor switch and the diode are ideal. The I–V characteristic of the composite switch is
An SCR is considered to be a semi controlled device because
The conduction loss versus device current characteristic of a power MOSFET is best approximated by
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is used as a power control switch by biasing it in cut-off region (OFF state) or in the saturation region (ON state). In the ON state, for the BJT,
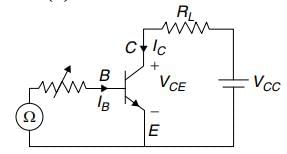
The triggering circuit of a thyristor is shown in figure. The thyristor requires a gate current of 10 mA, for guaranteed turn-on. The value of R required for the thyristor to turn on reliably under all conditions of Vb variation is
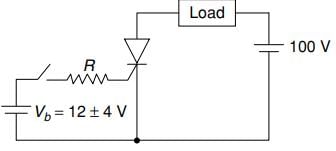
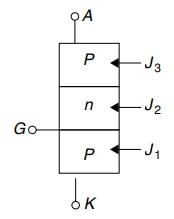
Figure shows a thyristor with the standard terminations of anode (A), cathode (K), gate (G) and the different junctions named J1 , J2 and J3 . When the thyristor is turned on and conducting