टेस्ट: कक्षा 8 सामान्य विज्ञान NCERT आधारित - 1 - UPSC MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - टेस्ट: कक्षा 8 सामान्य विज्ञान NCERT आधारित - 1
भारत में, फसलों को दो समूहों में वर्गीकृत किया जाता है, मौसम के आधार पर वे बढ़ती हैं-रबी फसलें और खरीफ फसलें। इन फसलों के संदर्भ में, निम्नलिखित कथनों पर विचार करें:
1. खरीफ की फसलें गर्मियों में बोई जाती हैं।
2. रबी की फसलें सर्दियों में उगाई जाती हैं।
ऊपर दिए गए कथनों में से कौन सा सही है / हैं?
In India, crops are classified into two groups, depending on the season they grow – Rabi crops and Kharif crops. With reference to these crops, consider the following statements:
1. Kharif crops are sown in summer.
2. Rabi crops are grown in winter.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
जैविक खाद के संबंध में, निम्नलिखित कथनों पर विचार करें:
1. यह मिट्टी की जल धारण क्षमता को बढ़ाता है।
2. यह मिट्टी को ढीला और छिद्रपूर्ण बनाता है।
3. यह दोस्ताना रोगाणुओं की संख्या को बढ़ाता है।
ऊपर दिए गए कथनों में से कौन सा सही है / हैं?
With respect to organic manure, consider the following statements:
1. It increases the water holding capacity of the soil.
2. It makes the soil loose and porous.
3. It increases the number of friendly microbes.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
कॉड लिवर ऑयल में उच्च मात्रा में विटामिन डी होता है। निम्न में से किस जानवर से कॉड लिवर ऑयल प्राप्त होता है?
Cod liver oil contains high amounts of vitamin D. Cod liver oil is obtained from which of the following animals?
निम्नलिखित में से कौन एक परिरक्षक है जिसका उपयोग फलों के संरक्षण में जाम और जेली के रूप में किया जाता है?
Which of the following is a preservative used in the preservation of fruits such as jams and jellies?
बीन्स और मटर अधिमानतः नाइट्रोजन की कमी वाली मिट्टी में उगाए जाते हैं:
1. वे मिट्टी से अधिकांश नाइट्रोजन को अवशोषित करते हैं।
2. वे फलदार पौधे हैं।
3. उनके पास रूट नोड्यूल में राइजोबियम होता है जो वायुमंडलीय नाइट्रोजन को ठीक कर सकता है।
4. वे हरे पौधे हैं।
Beans and peas are preferably grown in soils deficient in nitrogen:
1. They absorb most of the nitrogen from the soil.
2. They are fruit plants.
3. They have rhizobium in the root nodule which can fix atmospheric nitrogen.
4. They are green plants.
निम्नलिखित में से किस फसल में नाइट्रोजन उर्वरक की आवश्यकता नहीं होती है?
Which of the following crops does not require nitrogen fertilizer?
निम्नलिखित में से कौन सा जोड़ा गलत है?
मिट्टी को ढीला करने और मोड़ने की प्रक्रिया को कहा जाता है:
The process of loosening and turning the soil is called:
निम्नलिखित में से कौन सा एक उपयोगी सूक्ष्मजीव है?
1. साल्मोनेला टाइफी
2. राइजोबियम
3. लैक्टोबैसिलस
4. राइनोवायरस
Which of the following is a useful microorganism?
1. Salmonella Typhi
2. Rhizobium
3. Lactobacillus
4. Rhinovirus
संचित अनाजों को कीड़ों और सूक्ष्मजीवों से बचाने के लिए किन पत्तियों का उपयोग किया जाता है?
Which leaves are used to protect stored grains from insects and microorganisms?
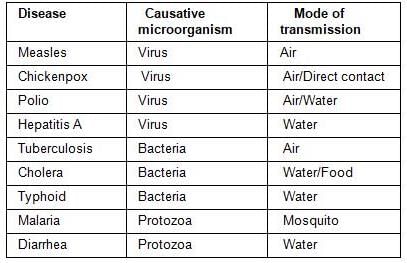
सूक्ष्मजीवों और उनके कारण होने वाली बीमारियों के संदर्भ में निम्नलिखित कथनों पर विचार करें:
1. चिकन पॉक्स और हेपेटाइटिस ए वायरस के कारण होते हैं।
2. टाइफाइड और मीजल्स बैक्टीरिया के कारण होते हैं।
3. डायरिया और मलेरिया प्रोटोजोआ के कारण होते हैं।
ऊपर दिए गए कथनों में से कौन सा सही है / हैं?
With reference to microorganisms and the diseases caused by them, consider the following statements:
1. Chicken pox and hepatitis A are caused by viruses.
2. Typhoid and measles are caused by bacteria.
3. Diarrhea and malaria are caused by protozoa.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
निम्नलिखित को धयान मे रखते हुए
1. शैवाल: स्पाइरोगाइरा
2. प्रोटोजोआ: क्लैमाइडोमोनस
3. कवक: प्रकंद (रोटी मोल्ड)
ऊपर दी गई कौन सी जोड़ी सही ढंग से मेल खाती है / हैं?
Keeping in view the following
1. Algae: Spirogyra
2. Protozoa: Chlamydomonas
3. Fungus: Rhizome (bread mold)
Which of the above pair(s) is/are correctly matched?
दूध को दही में बदलने के लिए निम्नलिखित में से किस सूक्ष्मजीव की आवश्यकता होती है?
Which of the following microorganism is required to convert milk into curd?
निम्नलिखित में से कौन सा खमीर द्वारा श्वसन द्वारा निर्मित होता है, जब इसे खाद्य पदार्थों के साथ मिलाया जाता है?
Which of the following is produced by yeast by respiration, when it is mixed with foods?
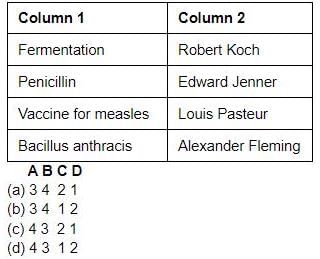
कॉलम 2 में उन लोगों के साथ कॉलम 1 में आइटम का मिलान करें, और सही विकल्प चुनें।