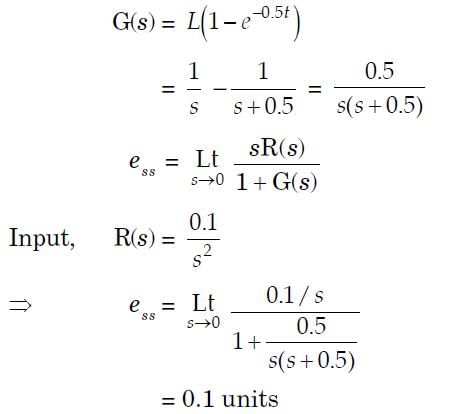Test: Basic Electrical Components - GATE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Basic Electrical Components
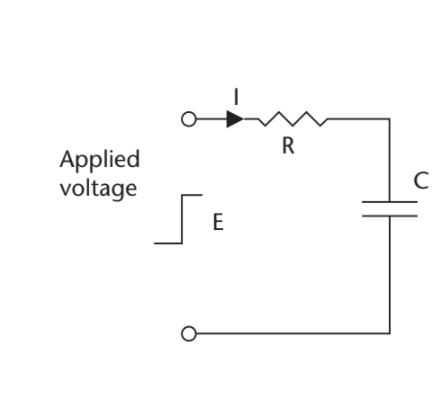
What is the voltage across the capacitor in the given figure 35s after the input voltage
steps from 0V to 54V, if the value of the resistor is 47 kΩ and the capacitor is 1.5F?

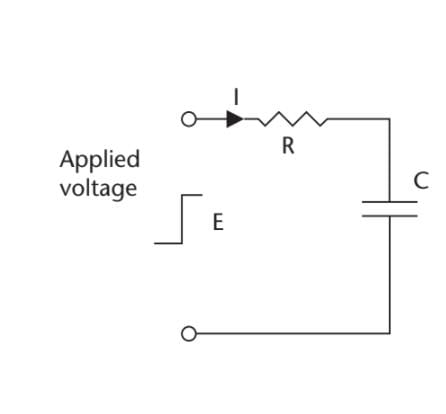
What is the time constant for the circuit shown in the given figure, if the resistor has a
value of 220 kΩ, and the capacitor is 2.2 F?

The resistive elements in a strain gauge are each 5kΩ. A digital voltmeter with ranges of 10V, 1V, and 0.1V, and a resolution of 0.1% of FSD, is used to measure the output voltage. If R2 is the fixed element and R1 is the element measuring strain, what is the minimum change in R1 that can be detected? Assume a supply of 10V.
Resistors R1 and R2 in the bridge circuit shown in the given figure are the strain gauge elements of 5kΩ each. Resistors R3 and R4 are fixed resistors, with values of 4.3 kW. A digital voltmeter with ranges of 10V, 1V, and 0.1V, and a resolution of 0.1% of FSD, is used to measure the output voltage. What is the minimum change in R1 that can be detected by the meter? Assume the supply E is 10V.
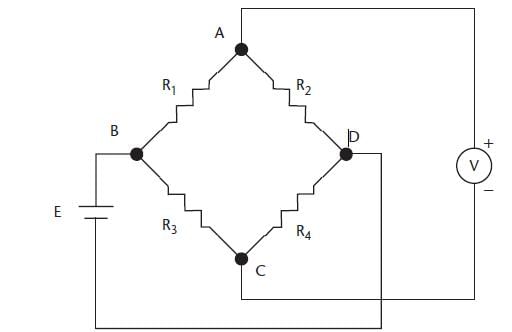
If the bridge circuit in the given figure is balanced, with R1 = 15 kΩ, R2 = 27 kΩ, R3= 18 kΩ, and C1 = 220 pF, what are the values of R4 and C2?
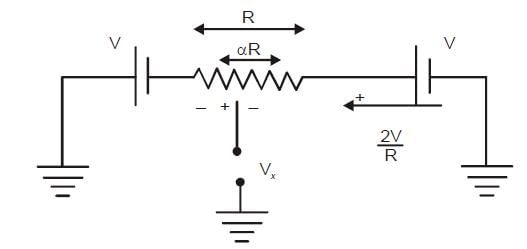
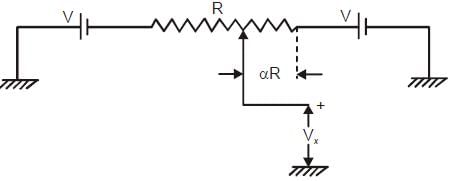
In the potentiometer circuit shown in the figure, the expression for Vx is
The response of a first-order measurement system to a unit step input is 1 – e– 0.5t, where t is in seconds. A ramp of 0.1 units per second is given as the input to this system. The error in the measured value after transients have died down is
A metal wire has a uniform cross-section A, length, and resistance R between its two endpoints. It is uniformly stretched so that its length becomes l. The new resistance is
A variable air gap type capacitor consists of two parallel plates: a fixed plate and a moving plate at a distance x. If a potential V is applied across the two plates, then the force of attraction between the plates is related to x as
The expression for the capacitance (C in pF) of a parallel plate capacitor is given by:
C = 6.94 × 10– 3 (d2/S). The diameter (d) of each plate is 20 mm and the spacing between the plates
(S) is 0.25 mm. The displacement sensitivity of the capacitor is approximate:
Which of the following can be measured using a Wheatstone bridge?
In a Wheatstone bridge, which of the following is used as a null detector?
Which of the following statements is correct for impedance?