Test: Memory Management- 2 - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Memory Management- 2
The minimum number of page frames that must be allocated to a running process in a virtual memory environment is determined by
Consider a system with a two-level paging scheme in which a regular memory access takes 150 nanoseconds, and servicing a page fault takes 8 milliseconds. An average instruction takes 100 nanoseconds of CPU time, and two memory accesses. The TLB hit ratio is 90%, and the page fault rate is one in every 10,000 instructions. What is the effective average instruction execution time?
A processor uses 2-level page tables for virtual to physical address translation. Page tables for both levels are stored in the main memory. Virtual and physical addresses are both 32 bits wide. The memory is byte addressable. For virtual to physical address translation, the 10 most significant bits of the virtual address are used as index into the first level page table while the next 10 bits are used as index into the second level page table. The 12 least significant bits of the virtual address are used as offset within the page. Assume that the page table entries in both levels of page tables are 4 bytes wide. Further, the processor has a translation look-aside buffer (TLB), with a hit rate of 96%. The TLB caches recently used virtual page numbers and the corresponding physical page numbers. The processor also has a physically addressed cache with a hit rate of 90%. Main memory access time is 10 ns, cache access time is 1 ns, and TLB access time is also 1 ns. Assuming that no page faults occur, the average time taken to access a virtual address is approximately (to the nearest 0.5 ns)
The optimal page replacement algorithm will select the page that
The process of assigning load addresses to the various parts of the program and adjusting the code and date in the program to reflect the assigned addresses is called
A computer system implements a 40 bit virtual address, page size of 8 kilobytes, and a 128-entry translation look-aside buffer (TLB) organized into 32 sets each having four ways. Assume that the TLB tag does not store any process id. The minimum length of the TLB tag in bits is _________
Consider six memory partitions of size 200 KB, 400 KB, 600 KB, 500 KB, 300 KB, and 250 KB, where KB refers to kilobyte. These partitions need to be allotted to four processes of sizes 357 KB, 210 KB, 468 KB and 491 KB in that order. If the best fit algorithm is used, which partitions are NOT allotted to any process?
Consider a fully associative cache with 8 cache blocks (numbered 0-7) and the following sequence of memory block requests: 4, 3, 25, 8, 19, 6, 25, 8, 16, 35, 45, 22, 8, 3, 16, 25, 7 If LRU replacement policy is used, which cache block will have memory block 7?
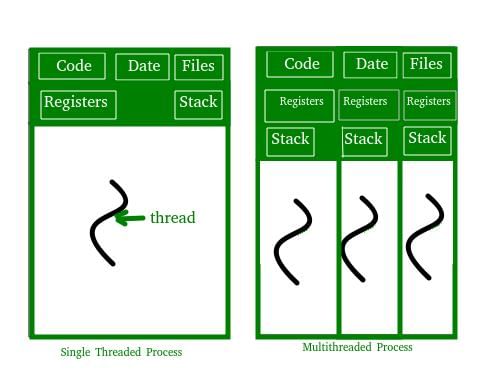
Which one of the following is NOT shared by the threads of the same process?
A disk has 200 tracks (numbered 0 through 199). At a given time, it was servicing the request of reading data from track 120, and at the previous request, service was for track 90. The pending requests (in order of their arrival) are for track numbers. 30 70 115 130 110 80 20 25. How many times will the head change its direction for the disk scheduling policies SSTF(Shortest Seek Time First) and FCFS (First Come Fist Serve)
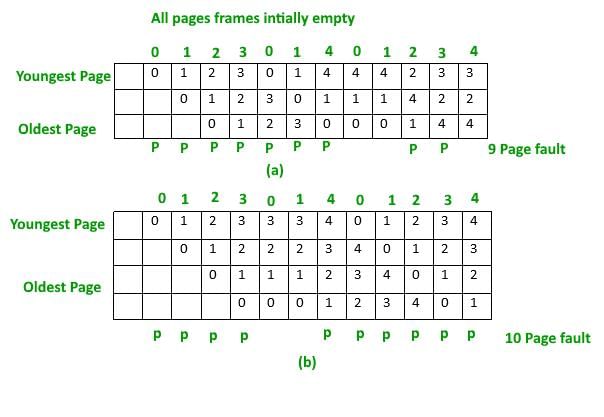
Consider a computer system with ten physical page frames. The system is provided with an access sequence a1, a2, ..., a20, a1, a2, ..., a20), where each ai number. The difference in the number of page faults between the last-in-first-out page replacement policy and the optimal page replacement policy is __________ [Note that this question was originally Fill-in-the-Blanks question]
In which one of the following page replacement algorithms it is possible for the page fault rate to increase even when the number of allocated frames increases?
A paging scheme uses a Translation Look-aside Buffer (TLB). A TLB-access takes 10 ns and a main memory access takes 50 ns. What is the effective access time(in ns) if the TLB hit ratio is 90% and there is no page-fault?
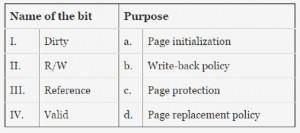
Match the following flag bits used in the context of virtual memory management on the left side with the different purposes on the right side of the table below.
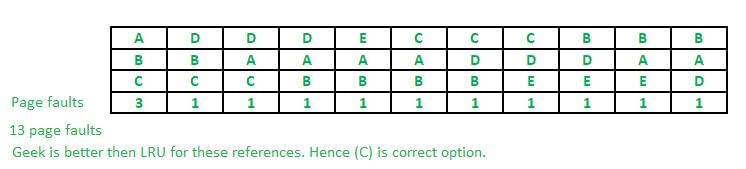
If LRU and Geek page replacement are compared (in terms of page faults) only for above reference string then find the correct statement from the following:
A multi-user, multi-processing operating system cannot be implemented on hardware that does not support:
a) Address translation
b) DMA for disk transfer
c) At least two modes of CPU execution (privileged and non-privileged).
d) Demand Paging
The overlay tree for a program is as shown below:
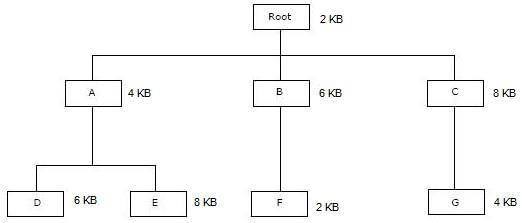
What will be the size of the partition (in physical memory) required to load (and run) this program?