Test: Stacks & Queues - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Stacks & Queues
Consider the following pseudocode that uses a stack
declare a stack of characters
while ( there are more characters in the word to read )
{
read a character
push the character on the stack
}
while ( the stack is not empty )
{
pop a character off the stack
write the character to the screen
}
What is output for input “geeksquiz”?
while ( there are more characters in the word to read )
{
read a character
push the character on the stack
}
while ( the stack is not empty )
{
pop a character off the stack
write the character to the screen
}
What is output for input “geeksquiz”?
Following is an incorrect pseudocode for the algorithm which is supposed to determine whether a sequence of parentheses is balanced:
declare a character stack
while ( more input is available)
{
read a character
if ( the character is a '(' )
push it on the stack
else if ( the character is a ')' and the stack is not empty )
pop a character off the stack
else
print "unbalanced" and exit
}
print "balanced"
Which of these unbalanced sequences does the above code think is balanced?
while ( more input is available)
{
read a character
if ( the character is a '(' )
push it on the stack
else if ( the character is a ')' and the stack is not empty )
pop a character off the stack
else
print "unbalanced" and exit
}
print "balanced"
The following postfix expression with single digit operands is evaluated using a stack:
8 2 3 ^ / 2 3 * + 5 1 * -
Note that ^ is the exponentiation operator. The top two elements of the stack after the first * is evaluated are:
Note that ^ is the exponentiation operator. The top two elements of the stack after the first * is evaluated are:
A single array A[1..MAXSIZE] is used to implement two stacks. The two stacks grow from opposite ends of the array. Variables top1 and top2 (topl< top 2) point to the location of the topmost element in each of the stacks. If the space is to be used efficiently, the condition for “stack full” is
To evaluate an expression without any embedded function calls:
A function f defined on stacks of integers satisfies the following properties. f(∅) = 0 and f (push (S, i)) = max (f(S), 0) + i for all stacks S and integers i.
If a stack S contains the integers 2, -3, 2, -1, 2 in order from bottom to top, what is f(S)?
Consider the following C program:
#include
#define EOF -1
void push (int); /* push the argument on the stack */
int pop (void); /* pop the top of the stack */
void flagError ();
int main ()
{ int c, m, n, r;
while ((c = getchar ()) != EOF)
{ if (isdigit (c) )
push (c);
else if ((c == '+') || (c == '*'))
{ m = pop ();
n = pop ();
r = (c == '+') ? n + m : n*m;
push (r);
}
else if (c != ' ')
flagError ();
}
printf("% c", pop ());
}
What is the output of the program for the following input ?
5 2 * 3 3 2 + * +
A priority queue Q is used to implement a stack S that stores characters. PUSH(C) is implemented as INSERT(Q, C, K) where K is an appropriate integer key chosen by the implementation. POP is implemented as DELETEMIN(Q). For a sequence of operations, the keys chosen are in
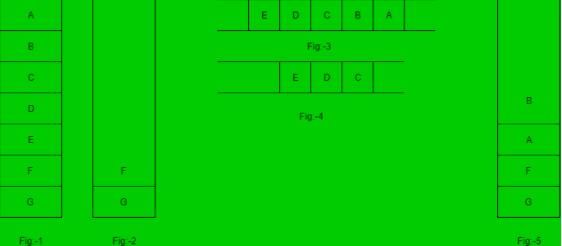
The seven elements A, B, C, D, E, F and G are pushed onto a stack in reverse order, i.e., starting from G. The stack is popped five times and each element is inserted into a queue.Two elements are deleted from the queue and pushed back onto the stack. Now, one element is popped from the stack. The popped item is ________.
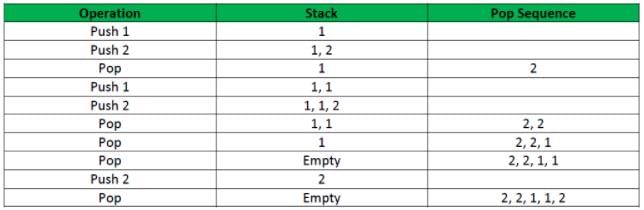
If the sequence of operations – push (1), push (2), pop, push (1), push (2), pop, pop, pop, push (2), pop are performed on a stack, the sequence of popped out values
Consider the following sequence of operations on an empty stack.
Push(54);push(52);pop();push(55);push(62);s=pop();
Consider the following sequence of operations on an empty queue.
enqueue(21);enqueue(24);dequeue();enqueue(28);enqueue(32);q=dequeue();
The value of s+q is ___________.
Convert the following infix expression into its equivalent post fix expression (A + B^ D) / (E – F) + G
The five items: A, B, C, D, and E are pushed in a stack, one after other starting from A. The stack is popped four items and each element is inserted in a queue. The two elements are deleted from the queue and pushed back on the stack. Now one item is popped from the stack. The popped item is
Stack A has the entries a, b, c (with a on top). Stack B is empty. An entry popped out of stack A can be printed immediately or pushed to stack B. An entry popped out of the stack B can be only be printed. In this arrangement, which of the following permutations of a, b, c are not possible?