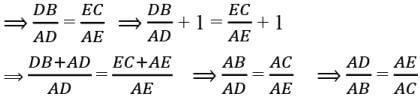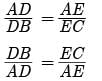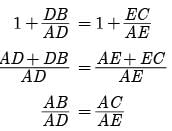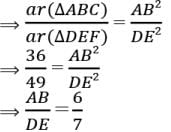Assertion & Reason Test: Triangles - 2 - Class 10 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Assertion & Reason Test: Triangles - 2
Direction: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion : Two similar triangle are always congruent.
Reason : If the areas of two similar triangles are equal then the triangles are congruent.
Direction: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion : ABC is an isosceles triangle right angled at C then AB2 = 2AC2.
Reason : If in a triangle, square of one side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the angle opposite the first side is a right angle.
Direction: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion : ΔABC is an isosceles triangle right angled of C , then AB2 = 2AC2.
Reason : In right ΔABC , right angled at B, AC2 =AB2 +BC2.
Direction: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion : ABC is an isosceles triangle with AC = BC. If AB2 = 2 AC2, then ΔABC is a right triangle.
Reason : If in a triangle, square of one side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the angle opposite the first side is a right angle.
Direction: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion : ΔABC ~ ΔDEF such that ar(ΔABC) = 36cm2 and ar(ΔDEF) = 49cm2 then, AB : DE = 6 :7
Reason : If ΔABC ~ ΔDEF , then ar(ΔABC)/ar(ΔDEF) = AB2/DE2 = BC2/EF2 = AC2/DF2
Direction: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion : In the ∆ABC , AB = 24 cm, BC = 7 cm and AC = 25 cm, then ∆ABC is a right angle triangle.
Reason : The ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides.
Direction: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion : In ∆ABC , DE|| BC such that AD = (7x - 4)cm, AE = (5 - 2)cm, DB = (3 + 4) cm and EC = 3 cm than x equal to 5.
Reason : If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distant point, than the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
Direction: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion : If a line intersects sides AB and AC of a Δ ABC at D and E respectively and is parallel to BC, then AD/AB = AE/AC
Reason : If a line is parallel to one side of a triangle then it divides the other two sides in the same ratio.
Direction: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion : Assertion : If in a ∆ABC , a line DE || BC , intersects AB in D and AC in E , then AB/AD = AC/AE
Reason : If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle intersecting the other two sides, then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
Direction: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion : ΔABC ~ ΔDEF such that ar(ΔABC) = 36cm2 and ar(ΔDEF) = 49cm2. Then, the ratio of their corresponding sides is 6 : 7
Reason : The ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides.