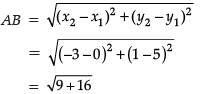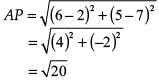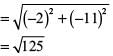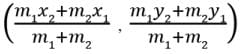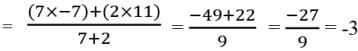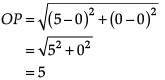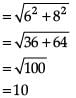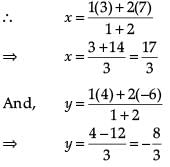Assertion & Reason Test: Coordinate Geometry - Grade 10 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Assertion & Reason Test: Coordinate Geometry
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): The ordinate of a point A on y-axis is 5 and B has coordinates (–3, 1). Then the length of AB is 5 units.
Reason (R): The point A(2, 7) lies on the perpendicular bisector of line segment joining the points P(6, 5) and Q(0, –4).
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion: The area of the triangle with vertices (-5, -1), (3, -5), and (5, 2) is 32 square units.
Reason: The point (x, y) divides the line segment joining the points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) in the ratio k : 1 externally, then
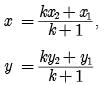
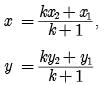
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion : The co-ordinates of the point which divides the join of A(-5, 11) and B(4,-7) in the ratio 7 : 2 is (2, -3) Reason : The coordinates of the point P(x, y) which divides the line segment joining the points A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2) in the ratio m1 : m2 is 

Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): △ABC with vertices A(–2, 0), B(2, 0) and C(0, 2) is similar to △DEF with vertices D(–4, 0), E(4, 0) and F(0, 4).
Reason (R): A circle has its centre at the origin and a point P(5, 0) lies on it. The point Q(6, 8) lies outside the circle.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion : The points (k, 2 -2k), (- k+ 1,2k) and (- 4 - k, 6 - 2k) are collinear if k = 1/2.
Reason : Three points A,B and C are collinear in same straight line, if AB + BC = AC.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion : If the points A(4, 3) and B(x, 5) lies on a circle with the centre O(2,3) then the value of x is 2.
Reason : The mid-point of the line segment joining the points P(x1, y1) and Q(x2, y2) is![]()
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): If the distance between the point (4, p) and (1, 0) is 5, then the value of p is 4.
Reason (R): The point which divides the line segment joining the points (7, – 6) and (3, 4) in ratio 1 : 2 internally lies in the fourth quadrant.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion : Centroid of a triangle formed by the points (a, b) (b, c), and (c, a) is at origin, Then a + b + c = 0 .
Reason : Centroid of a △ABC with vertices A (x1, y1), B(x2, y2) and C (x3, y3) is given by
![]()
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion : The possible values of x for which the distance between the points A(x, -1) and B(5, 3) is 5 units are 2 and 8.
Reason : Distance between two given points A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2) is given by,
![]()
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion : Mid-point of a line segment divides line in the ratio 1 : 1.
Reason : If area of triangle is zero that means points are collinear.