Case Based Questions Test: Principles of Inheritance & Variation - 1 - Grade 12 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Case Based Questions Test: Principles of Inheritance & Variation - 1
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
Mutation is sudden, discontinuous variation in genotype of an organism due to a change in its chromosomes and genes. Variation in DNA is a result of mutation. It is of three types : Gene mutation, chromosomal aberrations and gametic mutation. Gametic mutation is a change in chromosome number that brings effect on the phenotype, it is of two type - aneuploidy and euploidy. Mutation can be artificially produced by certain agents called mutagen. There are two major types of mutagens : physical and chemical mutagen.
Give one word for the following :
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
Mutation is sudden, discontinuous variation in genotype of an organism due to a change in its chromosomes and genes. Variation in DNA is a result of mutation. It is of three types : Gene mutation, chromosomal aberrations and gametic mutation. Gametic mutation is a change in chromosome number that brings effect on the phenotype, it is of two type - aneuploidy and euploidy. Mutation can be artificially produced by certain agents called mutagen. There are two major types of mutagens : physical and chemical mutagen.
Change in sequence of nucleotide in DNA is known as ...... .
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
Mutation is sudden, discontinuous variation in genotype of an organism due to a change in its chromosomes and genes. Variation in DNA is a result of mutation. It is of three types : Gene mutation, chromosomal aberrations and gametic mutation. Gametic mutation is a change in chromosome number that brings effect on the phenotype, it is of two type - aneuploidy and euploidy. Mutation can be artificially produced by certain agents called mutagen. There are two major types of mutagens : physical and chemical mutagen.
Aneuploidy which occurs due to loss of a complete homologous pair of chromosomes is:
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
Mutation is sudden, discontinuous variation in genotype of an organism due to a change in its chromosomes and genes. Variation in DNA is a result of mutation. It is of three types : Gene mutation, chromosomal aberrations and gametic mutation. Gametic mutation is a change in chromosome number that brings effect on the phenotype, it is of two type - aneuploidy and euploidy. Mutation can be artificially produced by certain agents called mutagen. There are two major types of mutagens : physical and chemical mutagen.
Which is the main category of mutation ?
Direction: Read the following and answer the questions given below:
During a study of inheritance of two genes, teacher asked students to perform an experiment. The students crossed white eyed, yellow bodied female Drosophila with a red eyed, brown bodied male Drosophila (i.e., wild). They observed that progenies in F2 generation had 1.3 percent recombinants and 98.7 percent parental type combinations. The experimental cross with results is shown in the given figure. [Note: Dominant wild type alleles are represented with (+) sign in superscript.]
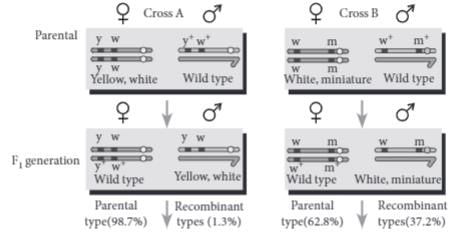
Assertion : When yellow bodied, white eyed Drosophila females were hybridised with brown-bodied, red eyed males; and F1 progeny was intercrossed , F2 ratio deviated from 9 : 3 : 3 : 1.
Reason : When two genes in a dihybrid are on the same chromosome, the proportion of parental gene combinations are much higher than the non-parental type.
Direction: Read the following and answer the questions given below:
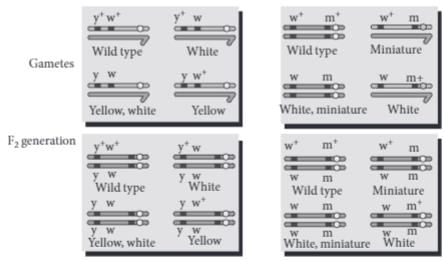
During a study of inheritance of two genes, teacher asked students to perform an experiment. The students crossed white eyed, yellow bodied female Drosophila with a red eyed, brown bodied male Drosophila (i.e., wild). They observed that progenies in F2 generation had 1.3 percent recombinants and 98.7 percent parental type combinations. The experimental cross with results is shown in the given figure. [Note: Dominant wild type alleles are represented with (+) sign in superscript.]
Genes white eyed and yellow bodied located very close to one another on the same chromosome tend to be transmitted together are called
Direction: Read the following and answer the questions given below:
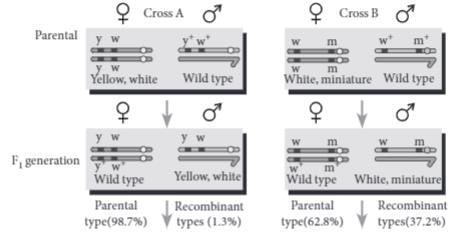
During a study of inheritance of two genes, teacher asked students to perform an experiment. The students crossed white eyed, yellow bodied female Drosophila with a red eyed, brown bodied male Drosophila (i.e., wild). They observed that progenies in F2 generation had 1.3 percent recombinants and 98.7 percent parental type combinations. The experimental cross with results is shown in the given figure. [Note: Dominant wild type alleles are represented with (+) sign in superscript.]
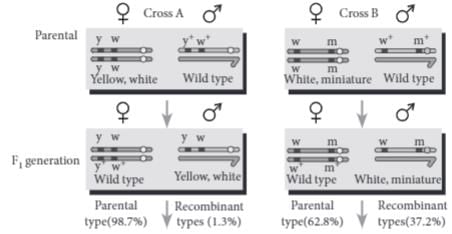
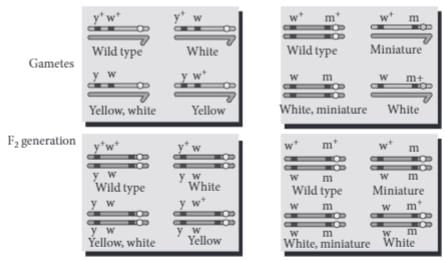
By conducting the given experiment, teacher can conclude that
A. Genes for eye colour and body colour are linked
B. Genes for eye colour and body colour show complete linkageC. Linked gene remain together and are inherited
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
Down syndrome (sometimes called Down’s syndrome) is a condition in which a child is born with an extra copy of their 21st chromosome hence its other name, trisomy 21. The affected individual mental retarded, short statured with small round, head, furrowed tongue and partially open mouth, Physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded.
Down syndrome is caused due to
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
Down syndrome (sometimes called Down’s syndrome) is a condition in which a child is born with an extra copy of their 21st chromosome hence its other name, trisomy 21. The affected individual mental retarded, short statured with small round, head, furrowed tongue and partially open mouth, Physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded.
Down syndrome is
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
Down syndrome (sometimes called Down’s syndrome) is a condition in which a child is born with an extra copy of their 21st chromosome hence its other name, trisomy 21. The affected individual mental retarded, short statured with small round, head, furrowed tongue and partially open mouth, Physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded.
Down Syndrome is an extra copy which chromosome
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
Down syndrome (sometimes called Down’s syndrome) is a condition in which a child is born with an extra copy of their 21st chromosome hence its other name, trisomy 21. The affected individual mental retarded, short statured with small round, head, furrowed tongue and partially open mouth, Physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded.
The number of chromosomes a child with Down syndrome has is
Direction: Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
Down syndrome (sometimes called Down’s syndrome) is a condition in which a child is born with an extra copy of their 21st chromosome hence its other name, trisomy 21. The affected individual mental retarded, short statured with small round, head, furrowed tongue and partially open mouth, Physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded.
One of this trait is seen in a person with Down syndrome
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason.
Assertion: A good example of multiple alleles is ABO blood group system.
Reason: When IA and IB alleles are present together in ABO blood group system, they both express their own types.
Dr. Patel is evaluating a 6-year-old child, Mia, who has been experiencing symptoms of chronic anemia, including fatigue, pallor, and delayed growth. Mia’s parents are concerned because these symptoms have persisted despite regular treatments. Mia’s family history reveals that her parents are both carriers of a genetic blood disorder, and several relatives have similar health issues.
Dr. Patel decides to perform genetic testing to identify the underlying cause of Mia's anemia. The test results indicate that Mia has an autosomal recessive blood disorder caused by a mutation in the globin genes. Specifically, the test shows that Mia's condition is related to the reduced production of α globin chains due to the deletion or mutation of genes on chromosome 16.
Based on Mia’s case, which of the following statements accurately describes the disorder she is likely to have?
Case:
Dr. Johnson is evaluating a 4-month-old infant, Lily, who has been showing developmental delays and unusual behavioral issues. Lily's parents are concerned because she has had a history of feeding difficulties and has not met developmental milestones expected for her age. After a thorough clinical evaluation, Dr. Johnson suspects a metabolic disorder.
To confirm the diagnosis, Dr. Johnson orders a series of tests, including a urine analysis. The results reveal elevated levels of phenylpyruvic acid and other related compounds in Lily's urine. Genetic testing shows that Lily has inherited a specific autosomal recessive disorder that results in a deficiency of an enzyme responsible for converting phenylalanine into tyrosine.
Based on Lily's case, which of the following statements correctly describes the metabolic disorder she is likely to have?




















