Assertion & Reason Test: Biomolecules - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Assertion & Reason Test: Biomolecules
Directions: This question consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering this question, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : D(+)– Glucose is dextrorotatory in nature.
Reason : ‘D’ represents its dextrorotatory nature.
Assertion : D(+)– Glucose is dextrorotatory in nature.
Reason : ‘D’ represents its dextrorotatory nature.
Directions: In this question, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Deoxyribose, C5H10O4 is not a carbohydrate.
Reason (R): Carbohydrates are optically active polyhydroxy aldehyde or polyhydroxy ketone or substances which give aldehyde or ketone on hydrolysis.
Assertion (A): Deoxyribose, C5H10O4 is not a carbohydrate.
Reason (R): Carbohydrates are optically active polyhydroxy aldehyde or polyhydroxy ketone or substances which give aldehyde or ketone on hydrolysis.
Directions: This question consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering this question, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion β-glycosidic linkage is present in maltose
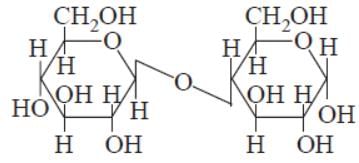
Reason : Maltose is composed of two glucose units in which C–1 of one glucose unit is linked to C–4 of another glucose unit.
Assertion β-glycosidic linkage is present in maltose

Directions: In this question, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): The two strands of DNA are complementary to each other.
Reason (R): The hydrogen bonds are formed between specific pairs of bases.
Directions: This question consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering this question, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : Vitamin D cannot be stored in our body
Reason : Vitamin D is fat soluble vitamin and is excreted from the body in urine
Directions: In this question, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Glycine must be taken through diet.
Reason (R): It is non-essential amino acid.
Directions: This question consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering this question, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : Sucrose is called an invert sugar.
Reason : On hydrolysis, sucrose bring the change in the sign of rotation from dextro (+) to laevo(–).
Directions: In this question, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Glucose reacts with hydroxylamine to form an oxime and also adds a molecule of hydrogen cyanide to give cyanohydrin.
Reason (R): The carbonyl group is present in the openchain structure of glucose.
Directions: This question consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering this question, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : At isoelectric point, the amino group does not migrate under the influence of electric field.
Reason : At isoelectric point, amino acid exists as a zwitterion.
Directions: In this question, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): All naturally occurring α amino acids except glycine are optically active.
Reason (R): Most naturally occurring α amino acids have L-configuration.