Assertion & Reason Test: Electromagnetic Induction - Grade 12 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Assertion & Reason Test: Electromagnetic Induction
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion(A): Faraday ’s laws of electromagnetic induction are consequences of law of conservation of energy.
Reason (R): The parameter LR in a L-R circuit has the dimension of time.
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Lenz’s law does not violets the principle of conservation of energy.
Reason (R): Induce e.m.f. never opposes the change in magnetic flux that causes the e.m.f.
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): When the magnetic flux changes around a metallic conductor, the eddy current is produced.
Reason (R): Electric potential determines the flow of charge.
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Mutual inductance becomes maximum when coils are wound on each other.
Reason (R): Mutual inductance is independent of orientation of coils.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion: Induced emf will always occur whenever there is change in magnetic flux.
Reason: Current always induces whenever there is change in magnetic flux.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion: Only a change in magnetic flux will maintain an induced current in the coil.
Reason: The presence of large magnetic flux through a coil maintain a current in the coil of the circuit is continuous.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : An induced current has a direction such that the magnetic field due to the current opposes the change in the magnetic flux that induces the current.
Reason : Above statement is in accordance with conservation of energy.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : Figure shows a horizontal solenoid connected to a battery and a switch. A copper ring is placed on a smooth surface, the axis of the ring being horizontal. As the switch is closed, the ring will move away from the solenoid.
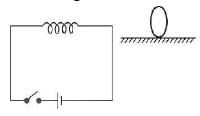
Reason : Induced emf in the ring, e=-dΦ/dt
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : Figure shows a metallic conductor moving in magnetic field. The induced emf across its ends is zero.
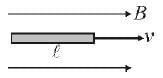
Reason : The induced emf across the ends of a conductor is given by e = Bvℓ sinθ.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : An induced emf appears in any coil in which the current is changing.
Reason : Self induction phenomenon obeys Faraday’s law of induction.



















