Case Based Questions Test: Our Environment - 2 - Super TET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Case Based Questions Test: Our Environment - 2
Read the following passage given below and answer the questions:
A water body characterized by nutrient rich water supports abundant growth of phytoplanktons and other water plants on its surface. Over time, the water body gets filled with a large number of such plants and the process is called Eutrophication. In such water bodies, dissolved oxygen content is nil or very less.
Q. In eutrophicated water body, growth rate of phytoplankton is high because of:
Read the following passage given below and answer the questions:
A water body characterized by nutrient rich water supports abundant growth of phytoplanktons and other water plants on its surface. Over time, the water body gets filled with a large number of such plants and the process is called Eutrophication. In such water bodies, dissolved oxygen content is nil or very less.
Q. There is an extremely low level of dissolved oxygen in a eutrophicated water body because:
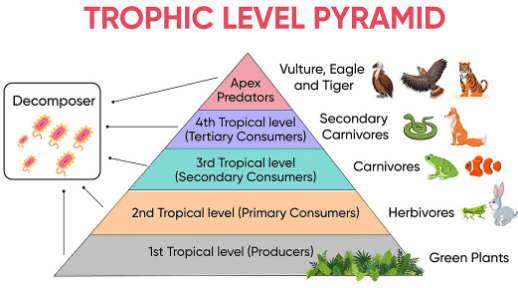
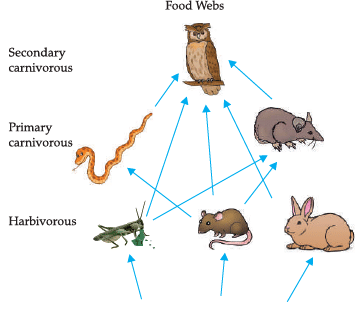
Study the following food web and answer the questions :
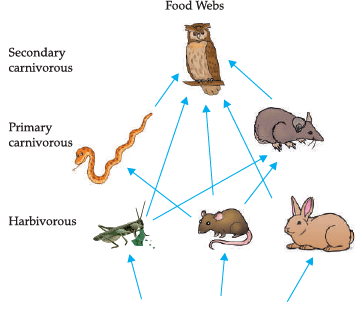
Which of these is the producer?

Study the following food web and answer the questions :
Which organisms represent top level carnivores?
Study the following food web and answer the questions :
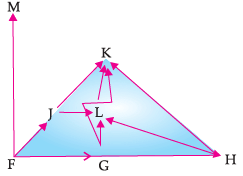
Which organisms are primary consumers?
Study the following food web and answer the questions :
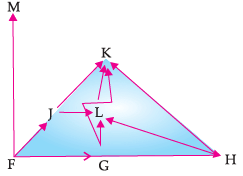
What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level?
Study the following food web and answer the questions :
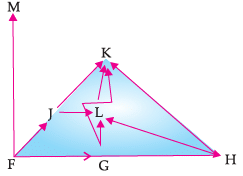
Which organisms will receive maximum energy in the ecosystem?
Read the following passage and answer the questions :
Human body is made up of five important components, of which water is the main component. Food as well as potable water is essential for every human being. The food is obtained from plants through agriculture; Pesticides are being used extensively for a high yield in the fields. These pesticides are absorbed by the plants from the soil along with water and minerals and from the water bodies these pesticides are taken up by the aquatic animals and plants. As these chemicals are not biodegradable, they get accumulated progressively at each trophic level. The maximum concentration of these chemicals gets accumulated in our bodies and greatly affects the health of our mind and body.
Q. Various steps in a food chain represent:
Read the following passage and answer the questions :
Human body is made up of five important components, of which water is the main component. Food as well as potable water is essential for every human being. The food is obtained from plants through agriculture; Pesticides are being used extensively for a high yield in the fields. These pesticides are absorbed by the plants from the soil along with water and minerals and from the water bodies these pesticides are taken up by the aquatic animals and plants. As these chemicals are not biodegradable, they get accumulated progressively at each trophic level. The maximum concentration of these chemicals gets accumulated in our bodies and greatly affects the health of our mind and body.
Q. With regard to various food chains operating in an ecosystem, man is a:
Waste management is essential in today ’s society. Due to an increase in population, the generation of waste is doubling day by day. Moreover, the increase in waste is affecting the lives of many people.
Waste management is the management of waste by disposal and recycling of it. Moreover, waste management needs proper techniques keeping in mind the environmental situations. For instance, there are various methods and techniques by which the waste is disposed of. You must have come across 5 R’s to save the environment: refuse, reduce, reuse, repurpose and recycle.
Q. Recycling of paper is a good practice but recycled paper should not be used as food packaging because
Waste management is essential in today ’s society. Due to an increase in population, the generation of waste is doubling day by day. Moreover, the increase in waste is affecting the lives of many people.
Waste management is the management of waste by disposal and recycling of it. Moreover, waste management needs proper techniques keeping in mind the environmental situations. For instance, there are various methods and techniques by which the waste is disposed of. You must have come across 5 R’s to save the environment: refuse, reduce, reuse, repurpose and recycle.
Q. The given graph shows the amount of waste generated, dumped and treated in percentage. Identify the reason for the low success rate of the waste management process.
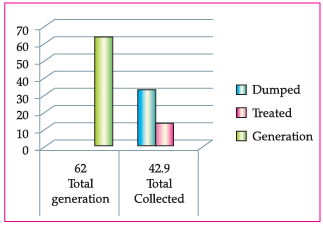
Waste management is essential in today ’s society. Due to an increase in population, the generation of waste is doubling day by day. Moreover, the increase in waste is affecting the lives of many people.
Waste management is the management of waste by disposal and recycling of it. Moreover, waste management needs proper techniques keeping in mind the environmental situations. For instance, there are various methods and techniques by which the waste is disposed of. You must have come across 5 R’s to save the environment: refuse, reduce, reuse, repurpose and recycle.
Q. Effective segregation of wastes at the point of generation is very important. Select the appropriate statements giving the importance of waste segregation.
(1) less waste goes to the landfills
(2) better for public health and the environment
(3) help in reducing the waste
(4) resulting in deterioration of a waste picker ’s health
Read the following and answer the questions:
Biosphere is a global ecosystem composed of living organisms and abiotic factors from which they derive energy and nutrients. An ecosystem is defined as a structural and functional unit of the biosphere consisting of living and non-living environments that interact by means of food chains and chemical cycles resulting in energy flow, biotic diversity and material cycling to form a stable, self-supporting system.
Biotic vs. Abiotic Factors

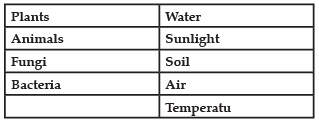
Q. Which trophic level is incorrectly defined?
Read the following and answer the questions:
Biosphere is a global ecosystem composed of living organisms and abiotic factors from which they derive energy and nutrients. An ecosystem is defined as a structural and functional unit of the biosphere consisting of living and non-living environments that interact by means of food chains and chemical cycles resulting in energy flow, biotic diversity and material cycling to form a stable, self-supporting system.
Biotic vs. Abiotic Factors

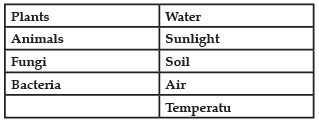
Q. Consider the following statements concerning food chains:
Which two of the above statements are correct?
(i) Removal of 80% tigers from an area resulted in greatly increased growth of vegetation
(ii) Removal of most of the carnivores resulted in an increased population of herbivores.
(iii) The length of the food chains is generally limited to 3 – 4 trophic levels due to energy loss
(iv) The length of the food chains may vary from 2 to 8 trophic levels
Read the following and answer the questions:
Biosphere is a global ecosystem composed of living organisms and abiotic factors from which they derive energy and nutrients. An ecosystem is defined as a structural and functional unit of the biosphere consisting of living and non-living environments that interact by means of food chains and chemical cycles resulting in energy flow, biotic diversity and material cycling to form a stable, self-supporting system.
Biotic vs. Abiotic Factors

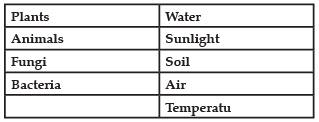
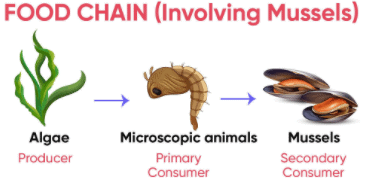
The diagram below shows a food web from the sea shore
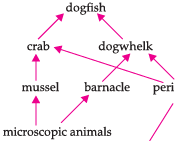
Q. The mussel can be described as
Read the following and answer the questions:
Biosphere is a global ecosystem composed of living organisms and abiotic factors from which they derive energy and nutrients. An ecosystem is defined as a structural and functional unit of the biosphere consisting of living and non-living environments that interact by means of food chains and chemical cycles resulting in energy flow, biotic diversity and material cycling to form a stable, self-supporting system.
Biotic vs. Abiotic Factors

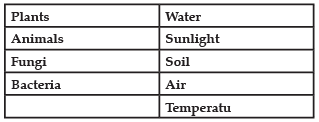
Q. Which of the following groups of organisms are not included in the ecological food chain?
Read the following and answer the questions:
Biosphere is a global ecosystem composed of living organisms and abiotic factors from which they derive energy and nutrients. An ecosystem is defined as a structural and functional unit of the biosphere consisting of living and non-living environments that interact by means of food chains and chemical cycles resulting in energy flow, biotic diversity and material cycling to form a stable, self-supporting system.
Biotic vs. Abiotic Factors

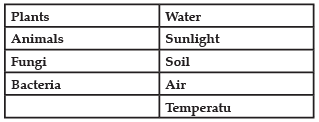
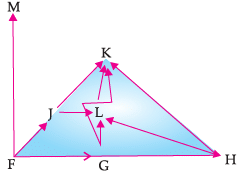
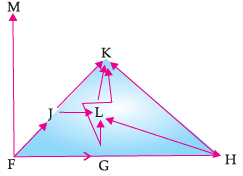
Q. The given figure best represents:
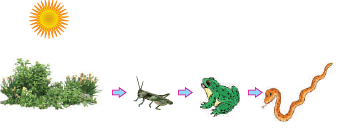
Read the following and answer the questions:
Food chains are very important for the survival of most species. When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction of a species in some cases. The foundation of the food chain consists of primary producers.
Primary producers, or autotrophs, can use either solar energy or chemical energy to create complex organic compounds, whereas species at higher trophic levels cannot and so must consume producers or other life that itself consumes producers. Because the sun's light is necessary for photosynthesis, most life could not exist if the sun disappeared. Even so, it has recently been discovered that there are some forms of life, chemotrophs, that appear to gain all their metabolic energy from chemosynthesis driven by hydrothermal vents, thus showing that some life may not require solar energy to thrive.
Q. If 10,000 J solar energy falls on green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem, what percentage of solar energy will be converted into food energy?
Read the following and answer the questions:
Food chains are very important for the survival of most species. When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction of a species in some cases. The foundation of the food chain consists of primary producers.
Primary producers, or autotrophs, can use either solar energy or chemical energy to create complex organic compounds, whereas species at higher trophic levels cannot and so must consume producers or other life that itself consumes producers. Because the sun's light is necessary for photosynthesis, most life could not exist if the sun disappeared. Even so, it has recently been discovered that there are some forms of life, chemotrophs, that appear to gain all their metabolic energy from chemosynthesis driven by hydrothermal vents, thus showing that some life may not require solar energy to thrive.
Q. Matter and energy are two fundamental inputs of an ecosystem. Movement of
Read the following and answer the questions:
Food chains are very important for the survival of most species. When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction of a species in some cases. The foundation of the food chain consists of primary producers.
Primary producers, or autotrophs, can use either solar energy or chemical energy to create complex organic compounds, whereas species at higher trophic levels cannot and so must consume producers or other life that itself consumes producers. Because the sun's light is necessary for photosynthesis, most life could not exist if the sun disappeared. Even so, it has recently been discovered that there are some forms of life, chemotrophs, that appear to gain all their metabolic energy from chemosynthesis driven by hydrothermal vents, thus showing that some life may not require solar energy to thrive.

Q. Mr. X is eating curd/yogurt. For this food intake in a food chain he should be considered as occupying