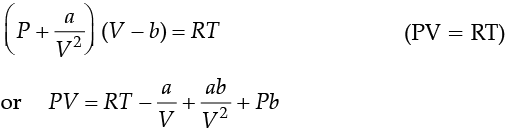Case Based Questions Test: States of Matter (Old NCERT) - Class 11 MCQ
8 Questions MCQ Test - Case Based Questions Test: States of Matter (Old NCERT)
Real gases do not obey the gas equation PV = nRT. The extent of deviation is measured in terms of compressibility factor (Z). The Van Der Waal’s equation describes the behaviour of real gases. The liquefaction of the gases depends upon the value of Van Der Waal’s constant 'a' and 'b'. Answer the given questions (i) to (iv).
Q. Which set of conditions represent easiest way to liquefy a gas?
Real gases do not obey the gas equation PV = nRT. The extent of deviation is measured in terms of compressibility factor (Z). The Van Der Waal’s equation describes the behaviour of real gases. The liquefaction of the gases depends upon the value of Van Der Waal’s constant 'a' and 'b'. Answer the given questions (i) to (iv).
Q. If Vo and Vi are the observed and ideal gas molar volume respectively, then Z for the gas is:
Real gases do not obey the gas equation PV = nRT. The extent of deviation is measured in terms of compressibility factor (Z). The Van Der Waal’s equation describes the behaviour of real gases. The liquefaction of the gases depends upon the value of Van Der Waal’s constant 'a' and 'b'. Answer the given questions (i) to (iv).
Q. If V is the molar volume of the gas and gas obeys Van Der Waal’s equation, the intercept of the plot PV(y-axis) versus P (x-axis) is:
Real gases do not obey the gas equation PV = nRT. The extent of deviation is measured in terms of compressibility factor (Z). The Van Der Waal’s equation describes the behaviour of real gases. The liquefaction of the gases depends upon the value of Van Der Waal’s constant 'a' and 'b'. Answer the given questions (i) to (iv).
Q. The compressibility of a gas is less than unity at STP. Therefore:
Viscosity is the internal resistance to the flow possessed by a liquid. The internal resistance depends upon the intermolecular attractive forces. Liquids which flow rapidly have low internal resistance, small intermolecular forces and low viscosity. Glass is an extremely viscous liquid, hence, its properties resemble to that of solids.
Assertion: Effusion rate of Oxygen is smaller than nitrogen.
Reason: Molecular size of Nitrogen is smaller than Oxygen.
Viscosity is the internal resistance to the flow possessed by a liquid. The internal resistance depends upon the intermolecular attractive forces. Liquids which flow rapidly have low internal resistance, small intermolecular forces and low viscosity. Glass is an extremely viscous liquid, hence, its properties resemble to that of solids.
Assertion: Vapour pressure is the characteristic property of liquids.
Reason: It does not depend upon the quantity of the liquid.
Viscosity is the internal resistance to the flow possessed by a liquid. The internal resistance depends upon the intermolecular attractive forces. Liquids which flow rapidly have low internal resistance, small intermolecular forces and low viscosity. Glass is an extremely viscous liquid, hence, its properties resemble to that of solids.
Assertion: Viscosity of the liquid decreases with decrease in temperature.
Reason: Kinetic energy of the molecules increases with increase in temperature.
Viscosity is the internal resistance to the flow possessed by a liquid. The internal resistance depends upon the intermolecular attractive forces. Liquids which flow rapidly have low internal resistance, small intermolecular forces and low viscosity. Glass is an extremely viscous liquid, hence, its properties resemble to that of solids.
Assertion: Viscosity of water is higher than ethanol.
Reason: Intermolecular forces in water are greater than ethanol.