Assertion & Reason Test: Hydrocarbons - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Assertion & Reason Test: Hydrocarbons
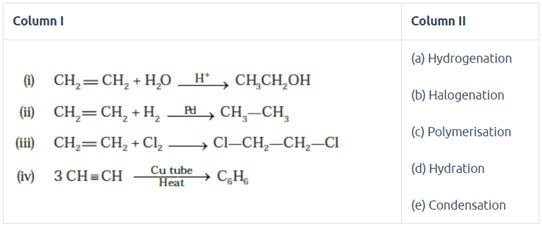
Match the reagent from Column I which on reaction with CH3—CH = CH2 gives some product given in Column II as per the codes given below:


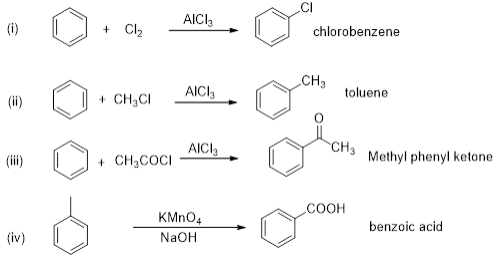
Match the following reactants in Column I with the corresponding reaction products in Column II.
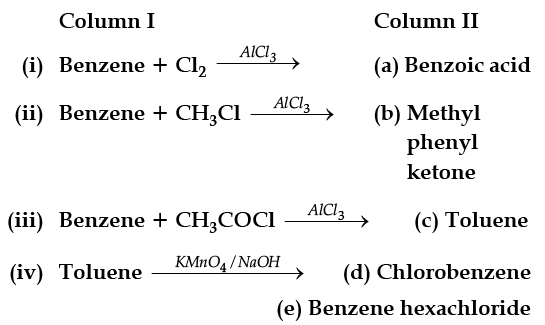

Match the reactions given in Column I with the reaction types in Column II.

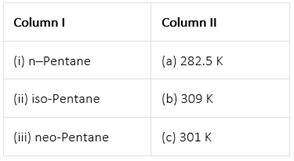
Match the hydrocarbons in Column I with the boiling points given in Column II.
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : The compound cyclooctane has the following structural formula :
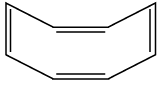
It is cyclic and has a conjugated 8π-electron system but it is not an aromatic compound.
Reason (R) : (4n + 2) π electrons rule does not hold good and the ring is not planar.
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : Nitration of benzene with nitric acid requires the use of concentrated sulphuric acid.
Reason (R) : The mixture of concentrated sulphuric acid and concentrated nitric acid produces the electrophile, NO2+.
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : Among isomeric pentanes, 2, 2-dimethylpentane has the highest boiling point.
Reason (R) : Branching does not affect the boiling point.
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : Toluene on Friedel-Crafts methylation gives o– and p–xylene.
Reason (R) : CH3-group bonded to the benzene ring increases electron density at o– and p– position.
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion: Saturated hydrocarbons are chemically less reactive.
Reason : All isomeric paraffins have same parent name.
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion : H2O2 has higher boiling point than water.
Reason : H2O2 has stronger dipole-dipole interactions than that shown by water.