Case Based Questions Test: Ray Optics & Optical Instruments - 1 - Grade 12 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Case Based Questions Test: Ray Optics & Optical Instruments - 1
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
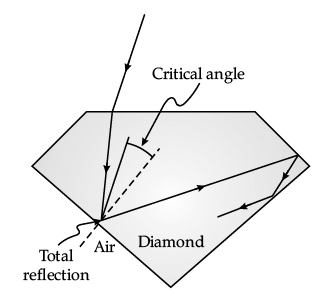
Sparking Brilliance of Diamond: The total internal reflection of the light is used in polishing diamonds to create a sparking brilliance.
By polishing the diamond with specific cuts, it is adjusted the most of the light rays approaching the surface are incident with an angle of incidence more than critical angle. Hence, they suffer multiple reflections and ultimately come out of diamond from the top. This gives the diamond a sparking brilliance.
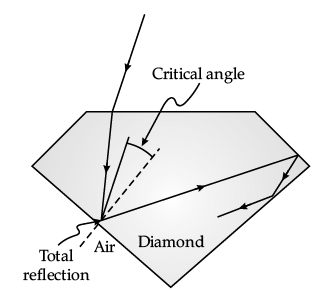
Q. The critical angle for a diamond is 24.4°. Then its refractive index is:

Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Sparking Brilliance of Diamond: The total internal reflection of the light is used in polishing diamonds to create a sparking brilliance.
By polishing the diamond with specific cuts, it is adjusted the most of the light rays approaching the surface are incident with an angle of incidence more than critical angle. Hence, they suffer multiple reflections and ultimately come out of diamond from the top. This gives the diamond a sparking brilliance.
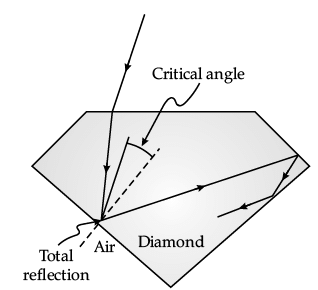
Q. A diamond is immersed in a liquid with a refractive index greater than water. Then the critical angle for total internal reflection will:

Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Sparking Brilliance of Diamond: The total internal reflection of the light is used in polishing diamonds to create a sparking brilliance.
By polishing the diamond with specific cuts, it is adjusted the most of the light rays approaching the surface are incident with an angle of incidence more than critical angle. Hence, they suffer multiple reflections and ultimately come out of diamond from the top. This gives the diamond a sparking brilliance.
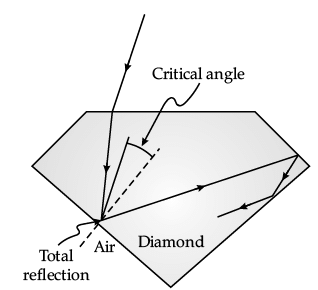
Q. Light cannot easily escape a diamond without multiple internal reflections. This is because:

Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Sparking Brilliance of Diamond: The total internal reflection of the light is used in polishing diamonds to create a sparking brilliance.
By polishing the diamond with specific cuts, it is adjusted the most of the light rays approaching the surface are incident with an angle of incidence more than critical angle. Hence, they suffer multiple reflections and ultimately come out of diamond from the top. This gives the diamond a sparking brilliance.
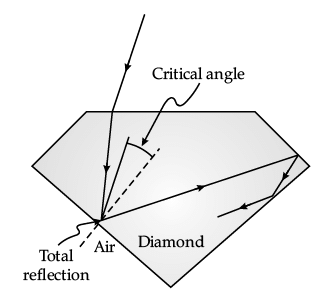
Q. The basic reason for the extraordinary sparkle of suitably cut diamond is that:
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Sparking Brilliance of Diamond: The total internal reflection of the light is used in polishing diamonds to create a sparking brilliance.
By polishing the diamond with specific cuts, it is adjusted the most of the light rays approaching the surface are incident with an angle of incidence more than critical angle. Hence, they suffer multiple reflections and ultimately come out of diamond from the top. This gives the diamond a sparking brilliance.
Q. The following diagram shows same diamond cut in two different shapes.
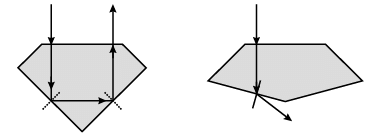
The brilliance of diamond in the second diamond will be:
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Photometry:
The measurement of light as perceived by human eye is called photometry. Photometry is measurement of a physiological phenomenon, being the stimulus of light as received by the human eye, transmitted by the optic nerves and analysed by the brain. The main physical quantities in photometry are (i) the luminous intensity of the source, (ii) the luminous flux or flow of light from the source and (iii) illuminance of the surface. The SI unit of luminous intensity (I) is candela (cd). The candela is the luminous intensity, in a given direction, of a source that emits monochromatic radiation of frequency 540 × 1012 Hz and that has a radiant intensity in that direction of 1/683 watt per steradian. If a light source emits one candela of luminous intensity into a solid angle of one steradian, the total luminous flux emitted into that solid angle is one lumen (lm). A standard 100 watt incandescent light bulb emits approximately 1700 lumens.
Q. Light received by human eye is analysed by:
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Photometry:
The measurement of light as perceived by human eye is called photometry. Photometry is measurement of a physiological phenomenon, being the stimulus of light as received by the human eye, transmitted by the optic nerves and analysed by the brain. The main physical quantities in photometry are (i) the luminous intensity of the source, (ii) the luminous flux or flow of light from the source and (iii) illuminance of the surface. The SI unit of luminous intensity (I) is candela (cd). The candela is the luminous intensity, in a given direction, of a source that emits monochromatic radiation of frequency 540 × 1012 Hz and that has a radiant intensity in that direction of 1/683 watt per steradian. If a light source emits one candela of luminous intensity into a solid angle of one steradian, the total luminous flux emitted into that solid angle is one lumen (lm). A standard 100 watt incandescent light bulb emits approximately 1700 lumens.
Q. Unit of luminous flux is:
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Photometry:
The measurement of light as perceived by human eye is called photometry. Photometry is measurement of a physiological phenomenon, being the stimulus of light as received by the human eye, transmitted by the optic nerves and analysed by the brain. The main physical quantities in photometry are (i) the luminous intensity of the source, (ii) the luminous flux or flow of light from the source and (iii) illuminance of the surface. The SI unit of luminous intensity (I) is candela (cd). The candela is the luminous intensity, in a given direction, of a source that emits monochromatic radiation of frequency 540 × 1012 Hz and that has a radiant intensity in that direction of 1/683 watt per steradian. If a light source emits one candela of luminous intensity into a solid angle of one steradian, the total luminous flux emitted into that solid angle is one lumen (lm). A standard 100 watt incandescent light bulb emits approximately 1700 lumens.
Q. What is photometry?
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Photometry:
The measurement of light as perceived by human eye is called photometry. Photometry is measurement of a physiological phenomenon, being the stimulus of light as received by the human eye, transmitted by the optic nerves and analysed by the brain. The main physical quantities in photometry are (i) the luminous intensity of the source, (ii) the luminous flux or flow of light from the source and (iii) illuminance of the surface. The SI unit of luminous intensity (I) is candela (cd). The candela is the luminous intensity, in a given direction, of a source that emits monochromatic radiation of frequency 540 × 1012 Hz and that has a radiant intensity in that direction of 1/683 watt per steradian. If a light source emits one candela of luminous intensity into a solid angle of one steradian, the total luminous flux emitted into that solid angle is one lumen (lm). A standard 100 watt incandescent light bulb emits approximately 1700 lumens.
Q. The SI unit of luminous intensity is:
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Photometry:
The measurement of light as perceived by human eye is called photometry. Photometry is measurement of a physiological phenomenon, being the stimulus of light as received by the human eye, transmitted by the optic nerves and analysed by the brain. The main physical quantities in photometry are (i) the luminous intensity of the source, (ii) the luminous flux or flow of light from the source and (iii) illuminance of the surface. The SI unit of luminous intensity (I) is candela (cd). The candela is the luminous intensity, in a given direction, of a source that emits monochromatic radiation of frequency 540 × 1012 Hz and that has a radiant intensity in that direction of 1/683 watt per steradian. If a light source emits one candela of luminous intensity into a solid angle of one steradian, the total luminous flux emitted into that solid angle is one lumen (lm). A standard 100 watt incandescent light bulb emits approximately 1700 lumens.
Q. A standard 100 watt incandescent light bulb emits approximately:
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Optical Fibre:
Optical fibre works on the principle of total internal reflection. Light rays can be used to transmit a huge amount of data, but there is a problem here – the light rays travel in straight lines. So unless we have a long straight wire without any bends at all, harnessing this advantage will be very tedious. Instead, the optical cables are designed such that they bend all the light rays’ inwards (using TIR). Light rays travel continuously, bouncing off the optical fibre walls and transmitting end to end data. It is usually made of plastic or glass.
Modes of transmission: Single-mode fibre is used for long-distance transmission, while multi- mode fiber is used for shorter distances. The outer cladding of these fibres needs better protection than metal wires. Although light signals do degrade over progressing distances due to absorption and scattering. Then, optical Regenerator system is necessary to boost the signal.
Types of Optical Fibres: The types of optical fibers depend on the refractive index, materials used, and mode of propagation of light. The classification based on the refractive index is as follows:
Step Index Fibres: It consists of a core surrounded by the cladding, which has a single uniform index of refraction.
Graded Index Fibres: The refractive index of the optical fibre decreases as the radial distance from the fibre axis increases.
Q. For long-distance transmission:
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Optical Fibre:
Optical fibre works on the principle of total internal reflection. Light rays can be used to transmit a huge amount of data, but there is a problem here – the light rays travel in straight lines. So unless we have a long straight wire without any bends at all, harnessing this advantage will be very tedious. Instead, the optical cables are designed such that they bend all the light rays’ inwards (using TIR). Light rays travel continuously, bouncing off the optical fibre walls and transmitting end to end data. It is usually made of plastic or glass.
Modes of transmission: Single-mode fibre is used for long-distance transmission, while multi- mode fiber is used for shorter distances. The outer cladding of these fibres needs better protection than metal wires. Although light signals do degrade over progressing distances due to absorption and scattering. Then, optical Regenerator system is necessary to boost the signal.
Types of Optical Fibres: The types of optical fibers depend on the refractive index, materials used, and mode of propagation of light. The classification based on the refractive index is as follows:
Step Index Fibres: It consists of a core surrounded by the cladding, which has a single uniform index of refraction.
Graded Index Fibres: The refractive index of the optical fibre decreases as the radial distance from the fibre axis increases.
Q. In graded index optical fibre:
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Optical Fibre:
Optical fibre works on the principle of total internal reflection. Light rays can be used to transmit a huge amount of data, but there is a problem here – the light rays travel in straight lines. So unless we have a long straight wire without any bends at all, harnessing this advantage will be very tedious. Instead, the optical cables are designed such that they bend all the light rays’ inwards (using TIR). Light rays travel continuously, bouncing off the optical fibre walls and transmitting end to end data. It is usually made of plastic or glass.
Modes of transmission: Single-mode fibre is used for long-distance transmission, while multi- mode fiber is used for shorter distances. The outer cladding of these fibres needs better protection than metal wires. Although light signals do degrade over progressing distances due to absorption and scattering. Then, optical Regenerator system is necessary to boost the signal.
Types of Optical Fibres: The types of optical fibers depend on the refractive index, materials used, and mode of propagation of light. The classification based on the refractive index is as follows:
Step Index Fibres: It consists of a core surrounded by the cladding, which has a single uniform index of refraction.
Graded Index Fibres: The refractive index of the optical fibre decreases as the radial distance from the fibre axis increases.
Q. Optical fibre works on the principle of:
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Optical Fibre:
Optical fibre works on the principle of total internal reflection. Light rays can be used to transmit a huge amount of data, but there is a problem here – the light rays travel in straight lines. So unless we have a long straight wire without any bends at all, harnessing this advantage will be very tedious. Instead, the optical cables are designed such that they bend all the light rays’ inwards (using TIR). Light rays travel continuously, bouncing off the optical fibre walls and transmitting end to end data. It is usually made of plastic or glass.
Modes of transmission: Single-mode fibre is used for long-distance transmission, while multi- mode fiber is used for shorter distances. The outer cladding of these fibres needs better protection than metal wires. Although light signals do degrade over progressing distances due to absorption and scattering. Then, optical Regenerator system is necessary to boost the signal.
Types of Optical Fibres: The types of optical fibers depend on the refractive index, materials used, and mode of propagation of light. The classification based on the refractive index is as follows:
Step Index Fibres: It consists of a core surrounded by the cladding, which has a single uniform index of refraction.
Graded Index Fibres: The refractive index of the optical fibre decreases as the radial distance from the fibre axis increases.
Q. Optical fibre is made of:
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Optical Fibre:
Optical fibre works on the principle of total internal reflection. Light rays can be used to transmit a huge amount of data, but there is a problem here – the light rays travel in straight lines. So unless we have a long straight wire without any bends at all, harnessing this advantage will be very tedious. Instead, the optical cables are designed such that they bend all the light rays’ inwards (using TIR). Light rays travel continuously, bouncing off the optical fibre walls and transmitting end to end data. It is usually made of plastic or glass.
Modes of transmission: Single-mode fibre is used for long-distance transmission, while multi- mode fiber is used for shorter distances. The outer cladding of these fibres needs better protection than metal wires. Although light signals do degrade over progressing distances due to absorption and scattering. Then, optical Regenerator system is necessary to boost the signal.
Types of Optical Fibres: The types of optical fibers depend on the refractive index, materials used, and mode of propagation of light. The classification based on the refractive index is as follows:
Step Index Fibres: It consists of a core surrounded by the cladding, which has a single uniform index of refraction.
Graded Index Fibres: The refractive index of the optical fibre decreases as the radial distance from the fibre axis increases.
Q. Light signal through optical fibre may degrade due to:














