Test: Pregnancy and Embryonic Development (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Pregnancy and Embryonic Development (NCERT)
In a normal pregnant woman, the amount of total gonadotropin activity was assessed. The result expected was.
What are the mitotic divisions that a zygote undergoes called?
Which of the following hormones is not a secretion product of human placenta?
The daughter cells formed as a result of cleavage of a zygote are called ________
hCG, hPL and relaxin are produced in women
Fetus gets nourishment and oxygen through
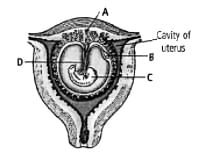
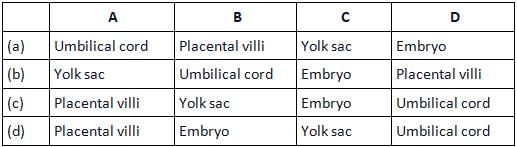
Identify the labelled parts A−D in the given figure of human foetus within the uterus.
What does inner cell mass give rise to?
Gastrula is the embryonic stage in which
Urine test during pregnancy determines the presence
Structure connecting the foetus to placenta is
During the development of embryo, which of the following occurs first?
External genital organs are developed during _________
Fetal movements can be observed during ____________



















