Test: Immunity (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Immunity (NCERT)
Identify the marking A, B, C and D in the figure given below and select the correct option.


Read the given statements carefully.
(i) Innate immunity is a specific type of defence, that is present at the time of birth.
(ii) Malignant malaria is caused by Plasmodium falciparum.
(iii) Malaria could be confirmed by Widal test.
(iv) Active immunity is slow and takes time to give its full effective response.
(v) Saliva in the mouth acts as physiological barrier for pathogens.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(ii) Malignant malaria is caused by Plasmodium falciparum.
(iii) Malaria could be confirmed by Widal test.
(iv) Active immunity is slow and takes time to give its full effective response.
(v) Saliva in the mouth acts as physiological barrier for pathogens.
Which of the following components does not participate in innate immunity?
Use of vaccines and immunisation programmes have controlled which of the following infectious diseases?
The first line of defence in the immune system is provided by
Primary response produced due to first time encounter with a pathogen is of
Select the correct statements regarding the characteristics of acquired immunity.
(i) Cell-mediated immunity is responsible for acquired immunity.
(ii) It produces a primary response of low intensity.
(iii) Active and passive immunity are types of acquired immunity.
(iv) Polymorphonuclear leucocytes and natural killer cells are involved in acquired immunity.
Read the following statements regarding spleen and select the correct option.
(i) Spleen is a large bean-shaped organ which mainly contains lymphocytes and phagocytes.
(ii) Spleen is a large reservoir of erythrocytes.
(iii) Spleen is a primary lymphoid organ.
(iv) Spleen acts as a filter of the blood by trapping blood-borne microorganisms.
Which one of the following immune system components does not correctly match with its respective role?
Which out of the following groups represent auto immune disorders?
Which of the following cells actively participate during allergy?
Given below is the diagram of human lymphatic system, where A, B, C and D are lymphoid organs. Select incorrect option regarding the lymphoid organs labelled as A, B, C and D.
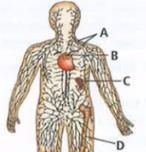
Which of these glands is large at the time of birth but in adults, it reduces to a very small size?
Which of the following statements regarding different barriers of innate immunity is not correct?



















