Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs): The Flower - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs): The Flower
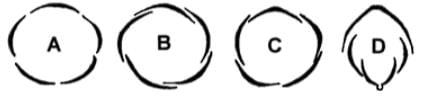
On the basis of relative position of different floral parts on the thalamus, a flower can be hypogynous, Perigynous or epigynous. With respect to the given figures (A, B, C and D), select the correct option:




If the gynoecium is present in the top most position of the thalamus, the flower is referred to as
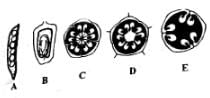
Identify the different types of placentations shown in figure and select the correct option.
Based on the position of floral parts on thalamus, the flowers, are described as hypogynous, perigynous and perigynous and epigynous. Which of the following floral forms (A-D) represent the flowers of Rose and Plum respectively?
Which of the following figures represent a typical placentation as seen in Hibiscus rosa sinensis (China rose)?
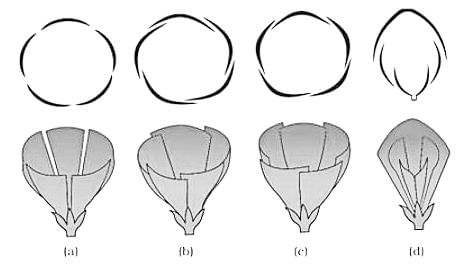
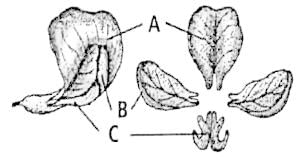
Select the correct option for A, B and C in the given diagram of papilionaceous corolla.
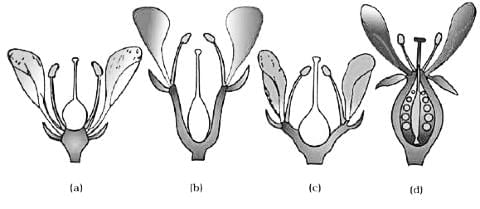
In _____ aestivation, sepals or petals in a whorl just touch one another at the margins, without overlapping, as is found in _____ .
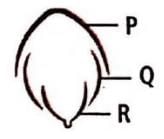
The given figure represents vexillary aestivation. Select the suitable labels for P, Q and R .
Identify the types of aestivation shown in the folowing diagram: