Test: Urine Formation (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Urine Formation (NCERT)
A large quantity of fluid is filtered everyday by nephrons in the kidneys but only about 1% of it is excreted as urine. The remaining 99% of the filtrate
Which one of the following statements in regard to the excretion by the human kidneys is correct?
Which one of the following is a correct pair showing the function of a specific part of the human nephron?
The given figure represents a single nephron. From a mammalian kidney. Identify the labelled parts, match them with the functions (i-iv) and select the correct option.
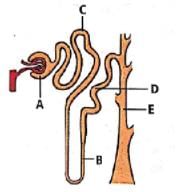
(i) The site of ultrafiltration.
(ii) Particularly sensitive to ADH.
(iii) the main site for the reabsorption of glucose and amino acids
(iv) Largely responsible for the maintenance of blood pH.
Effective filtration pressure in glomerulus is caused due to
The maximum amount of electrolytes and water (70-80 percent) from the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed in which part of the nephron?
A fall in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) activates
Which of the following options has the correct pair of nephron parts that maintain pH and ionic balance of blood? ,
Statement I: Collecting duct plays a role in the maintenance of osmolarity.
Statement II: The collecting duct allows the passsage of small amout of urea into the medullary interstitium.
Which of the following, is not a factor responsible for maintaining high osmolarity of the renal medulla?
(i) Active transport of salt from the upper region of the ascending limb.
(ii) The spatial arrangement of juxtamedullary nephrons
(iii) Diffusion of urea from the collecting duct.
(iv) Diffusion of salt from the descending limb of the loop of Henle.
The given figure shows reabsorption and secretion of major substances at different parts of the nephron. The movement of which of the following substances is wrongly depicted?
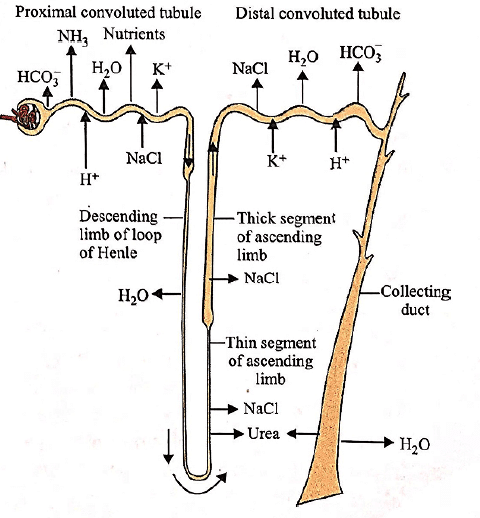
Of the total nephrons, juxtamedullary nephrons constitute
The net pressure gradient that causes the fluid to filter out of the glomeruli into the capsule is
Which of the following is removed from the filtrate at loop of Heenle?
Select the correct option representing the parts of nephron that respectively absorb
(i) Glucose,
(ii) Amino acids,
(iii) Inorganic ions (Na+, K+, Cl-) and
(iv) Urea in maximum
Hippuric acid, cretinines and ketones are added to urine through
Which of the following is the correct sequence of processes involved in urine formation?



















