Test: Regulation of Respiration (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Regulation of Respiration (NCERT)
During rest, the metabolic needs of the body are at their minimum. Which of the following is indicative of this situation?
Chemosensitive area of respiratory centre in medulla is affected by
Pneumotaxic centre which can moderate the functions of the respiratory rhythm centre is present at
What is the primary site for the exchange of gases in the human body?
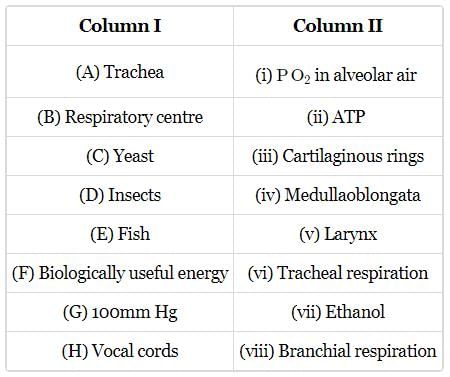
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
Partial pressure of oxygen in inspired and expired air is ....... and ....... mm of Hg.
Complete the following sentence by selecting the correct option.
The breathing rhythm is generated in the __(i)__ and is influenced by variation in levels of __(ii)___ in the blood.
Read the following four statements (i) - (iv) with certain mistakes in two of them.
(i) A water breather expends much more energy in ventilating its respiratory surface than an air-breathing one.
(ii) Lungs become empty after forceful expiration.
(iii) Exchange of gases in the lungs are interrupted during expiration.
Respiratory movement are controlled by CO2 concentration of arterial blood.
Which of the above two statements have mistakes?
Fill up the blanks in the following paragraph by selecting the correct option.
Human beings have a significant ability to maintain and moderate the respiratory rhythm to suit the demands of the body tissues. This is done by the neural system. A specialised centre present in the medulla region of the brain called ___(i) is primarily responsible for this regulation. Another centre present in the pons region of the brain called ___(ii)can moderate the functions of the respiratory rhytm centre. Neutral signal from this centre cen reduce the duration of )___(iii) and thereby alter the respiratory rate. A ___(iv) is situated adjacent to the rhythm centre which is highly sensitive to CO2 and hydrogen ions.
Rate of breathing is controlled mainly by ________________.




















