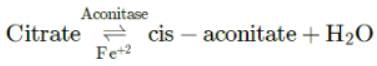Test: Aerobic Respiration - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Aerobic Respiration
Which of the following steps during glycolysis is associated with utilization of ATP?
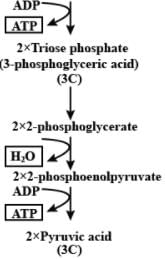
Which of the following conversions involve ATP synthesis during glycolysis?
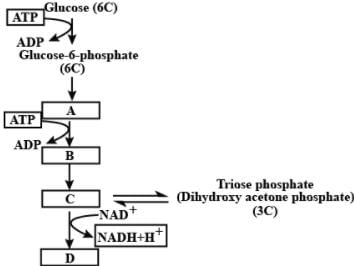
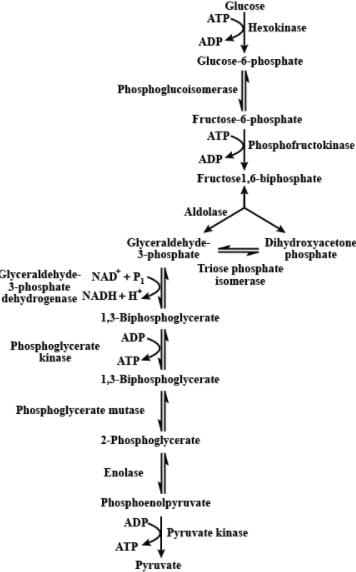
The flow chart given below shows the steps in glycolysis. Select the option that correctly fills in the missing steps A, B, C, and D.
Substrate level phosphorylation occurs during which step of Krebs' cycle?
The first 5C dicarboxylic acid in Krebs' cycle which is used in nitrogen metabolism is
Kreb’s cycle is also called metabolic sink as it is a common pathway for:
When two molecules of acetyl CoA enter the TCA cycle, net gain at the end of the cycle is
The respiration in germinating seeds produces energy, which can be detected in the form of
In Krebs cycle the FAD participates as electron acceptor during the conversion of
Krebs' cycle starts with the formation of a six carbon compound by reaction between
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Glycolysis occurs in mitochondrial matrix.
Statement 2: Kerbs' cycle occurs on cristae of mitochondria.
Categories the given equations under respective phases and select the correct option.
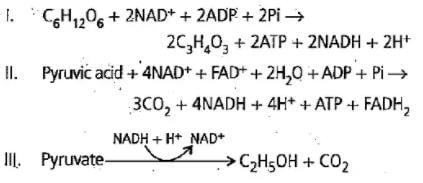
Which of the following steps of respiration is amphibolic?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Mitochondria is known as power house of cell.
Statement 2: ATP synthesis occurs in mitochondria.
Refer to the given figure and select the correct option for A,B,C and D.
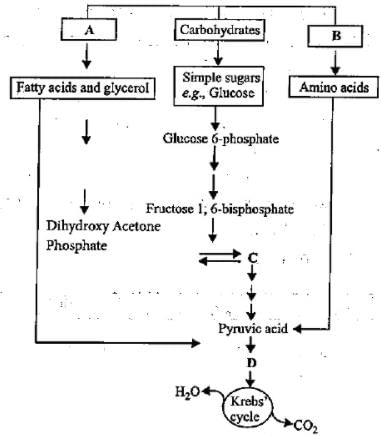
Which of the following cellular metabolic processes can occur both in the presence or absence of O2?
Consider the first reaction of TCA cycle.
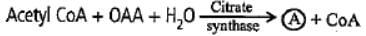
What is true about compound A?
During complete metabolism of glucose, the number of ATP formed is
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: During photophosphorylation (of photosynthesis), light energy is utilised for the production of a proton gradient during ATP synthesis.
Statement 2: In respiration, the energy of oxidation-reduction is utilised for the phosphorylation and thus the process is called oxidative phosphorylation.
Electron transport chain (ETC) is a set of ______ electron carriers present in a specific sequence along ______ mitochondrial membrane.


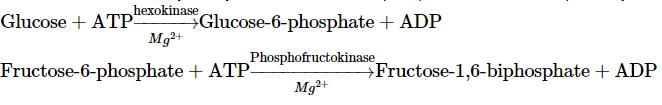

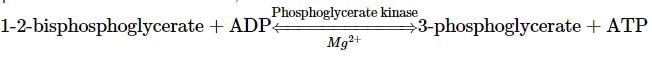
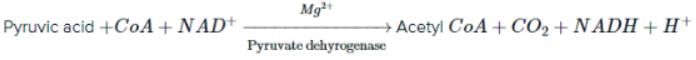
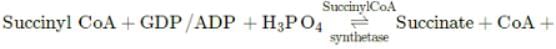 GTP/ATP
GTP/ATP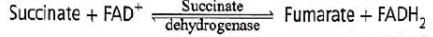
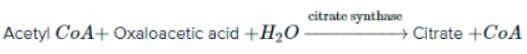
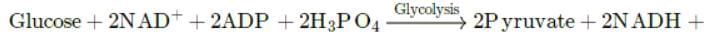 2ATP + 2H+
2ATP + 2H+