Test: Biotechnological Applications in Medicine & Industry (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Biotechnological Applications in Medicine & Industry (NCERT)
Which of the following statements regarding the structure of proinsulin and mature insulin are not correct?
(i) Proinsulin is made up of three polypeptide chains- A, B and C.
(ii) C - polypeptide chain with 33 amino adds is removed prior to insulin formation.
(iii) Mature insulin is made up of 51 amino acids arranged in two polypeptide chains- A and B.
(iv) Polypeptide chain A has 30 amino acids and polypeptide chain B has 21 amino acids.
(v) Polypeptide chains A and B are interconnected by only one S−S linkage.
(i) Proinsulin is made up of three polypeptide chains- A, B and C.
(ii) C - polypeptide chain with 33 amino adds is removed prior to insulin formation.
(iii) Mature insulin is made up of 51 amino acids arranged in two polypeptide chains- A and B.
(iv) Polypeptide chain A has 30 amino acids and polypeptide chain B has 21 amino acids.
(v) Polypeptide chains A and B are interconnected by only one S−S linkage.
Which of the following statements regarding gene therapy is/are correct?
Read the given statements and select the correct options
Statement 1: In recombinant DNA technology, human genes are often transferred into bacteria (prokaryotes) or yeast (eukaryote).
Statement 2: Both bacteria and yeast multiply very fast to form huge population which expresses the desired gene.
Statement 2: Both bacteria and yeast multiply very fast to form huge population which expresses the desired gene.
Read the given statements and select the correct option
Statement 1: PCR technique is helpful in detecting bacterial and viral diseases even when symptoms of the disease are not yet visible
Statement 2: Very low concentrations of bacteria or viruses in human body can be detected by amplification of their nucleic acids using the PCR technique
DNA fingerprinting refer to
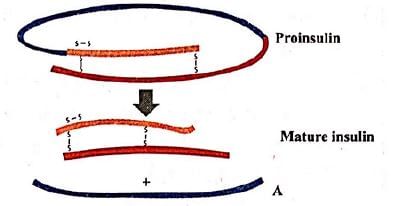
Given figure represents the maturation of pro-insulin into insulin. Identify the product A.
Early detection of a disease is possible by
Technique used to detect the DNA in a clone is
Which of the following statements is not correct?
What might be an advantage of beginning gene therapy prior to birth?
Which of the following companies started selling humulin in the year 1983?
Which of the following statements is incorrect about gene therapy in ADA deficiency?
The study of all the proteins coded by the genome is called as
Gene can therapy can be referred to as
For effective treatment of a disease
Some of the steps involved in the production of Humulin are given below. Choose the correct sequence.
(i) Synthesis of gene (DNA) for human insulin artificially.
(ii) Culturing recombinant E.coli in bioreactors.
(iii) Purification of humulin.
(iv) Insertion of human insulin gene into plasmid.
(v) Introduction of recombinant plasmid into E.coli.
(vi) Extraction of recombinant gene product from E.coli.
During the processing of proinsulin into the mature insulin
Study the following steps which are followed during the process of gene therapy while treating a patient of SCID
(i) Retrovirus infects lymphocytes extracted from bone marrow of the patient and cultured.
(ii) Engineered cells are injected into patient's bone marrow.
(iii) Normal allele is inserted into a retrovirus.
(iv) Retrovirus makes a DNA copy of its RNA. This DNA carrying the normal allele gets inserted into the chromosome of the host cell.
Arrange the above-given steps in correct sequence and select the correct answer.
A doctor while operating on an HIV (+)ve patient accidentally cuts himself with a scalpel. Suspecting himself to have contracted the virus which test will he take to rule out/confirm his suspicion?
Second generation vaccines are prepared by recombinant DNA technology. Which out of the following are the examples of such vaccines?




















