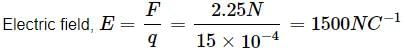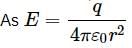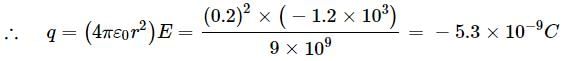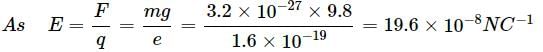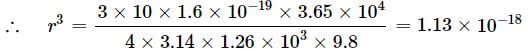Test: Electric Field (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electric Field (NCERT)
Electrical as well as gravitational affects acan be thought to be caused by fields. Which the following is true of an electrical or gravitational field?
If the charge on an object is doubled then electric field becomes
A force of 2.25 N acts on a charge of 15 x 10-4 C. The intensity of electric field at that point is
A conducting sphere of radius 10 cm has unknown charge. If the electric field at a distance 20 cm from the centre of the sphere is 1.2 x 103N C-1 and points radially inwards. The net charge on the sphere is
A particle of mass 10-3kg and charge 5μC is thrown at a speed of 20m s-1 against a uniform electric field of strength 2 x 105 N C-1. The distance travelled by particle before coming to rest is
An electron initially at rest falls a distance of 1.5 cm in a uniform electric field of magnitude 2 x 104N/C. The time taken by the electron to fall this distance is
The electric field that can balance a charged particle of mass 3.2 x 10-27 kg is (Given that the charge on the particle is 1.6 x 10-19 C)
An oil drop of 10 excess electrons is held stationary under a constant electric field of 3.65 x 104 N C-1 in Millikan's oil drop experiment. The density of oil is 1.26 g cm-3. Radius of the oil drop is
(Take, g = 9.8 m s-2, e = 1.6 x 10-19 C)
Five equal charges each of value q are placed at the corners of a regular pentagon of side a. The electric field at the centre of the pentagon is
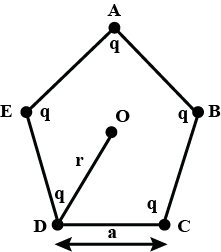
Five equal charges each of value q are placed at the corners of a regular pentagon of side a. What will be the electric field at centre O, if the charge from one of the corners (say A) is removed?
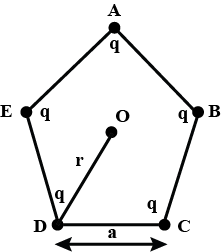
In the previous question , what will be the electric field at O if the charge q at A is replaced by -q?
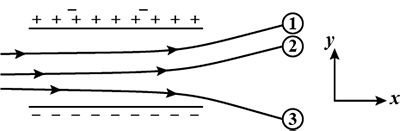
The tracks of three charged particles in a uniform electrostatic field as shown in the figure. Which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio?



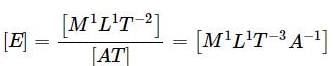
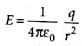
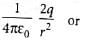 E' = 2E
E' = 2E