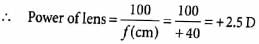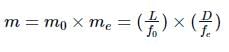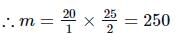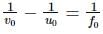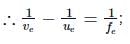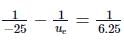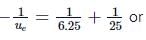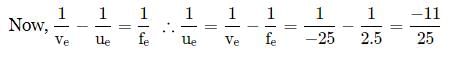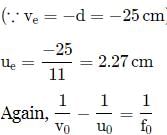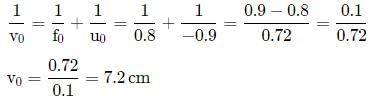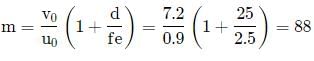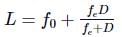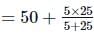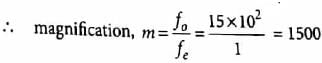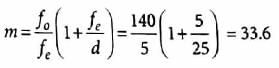Test: Optical Instruments (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Optical Instruments (NCERT)
Different objects at different distances are seen by the eye. The parameter that remains constant is
An under-water swimmer cannot see very clearly even in absolutely clear water because of
The nearer point of hypermetropic eye is 40 cm. The lens to be used for its correction should have the power?
A microscope is focused on a mark on a piece of paper and then a slab of glass of thickness 3 cm and refractive index 1.5 is placed over the mark. How should the microscope be moved to get the mark in focus again?
A compound microscope consists of an objective lens with focal length 1.0 cm and eye piece of focal length 2.0 cm and a tube length 20 cm the magnification will be
In a compound microscope, the focal lengths of two lenses are 1.5 cm and 6.25 cm. If an object is placed at 2 cm from objective and the final image is formed at 25 cm from eye lens, the distance between the two lenses is
A person with normal near point 25 cm using a compound microscope with objective of focal length 8.0 mm and an eye piece of focal length 2.5 cm can bring an object placed at 9.0 mm from the objective in sharp focus. The separation between two lenses and magnification respectively are
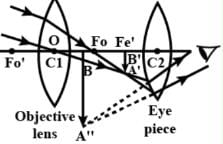
The final image in an astronomical telescope with respect to object is
In an astronomical telescope in normal adjustment, a straight black line of length L is drawn on the objeective lens. The eyepiece forms a real image of this line. The length of this image is l. The magnification of the telescope is
The focal length of the lenses of an astronomical telescope are 50 cm and 5 cm. The length of the telescope when the image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision is
A small telescope has an objective lens of focal length 144 cm and an eye piece of focal length 6.0 cm. What is the separation between the objective and the eye piece?
An astronomical refractive telescope has an objective of focal length 20m and an eyepiece of focal length 2cm.
A giant refracting telescope at an observatory has an objective lens of focal length 15 m. If an eye piece of focal length 1.0 cm is used, what is the angular magnification of the telescope?
A small telescope has an objective lens of focal length 140 cm and an eyepiece of focal length 5.0 cm. The magnifying power of the telescope for viewing distant objects when the final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision 25 cm will be
A reflecting telescope has a large mirror for its objective with radius of curvature equal to 80 cm. The magnifying power of this telescope if eye piece used has a focal length of 1.6 cm is