Test: Geography- 9 - UPSC MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Geography- 9
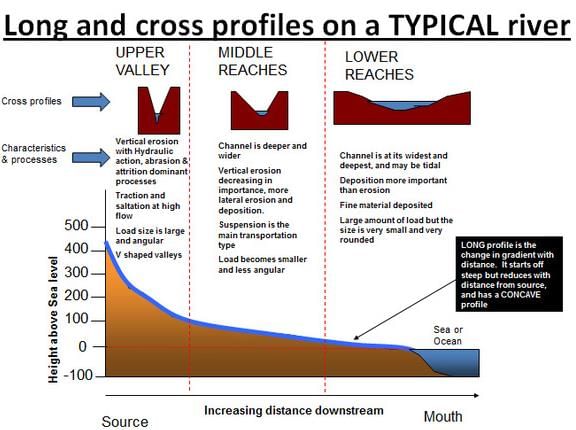
Consider the following features in a drainage system.
- Interlocking spurs
- Ox-bow lakes
- River cliffs
- Rapids and waterfalls
Which of the above will be found in the middle course of the river system?
Which of the following cannot be the use of Lagoons and backwaters?
- Fishing
- Irrigation of paddy crops
- Navigation
Select the correct answer code:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Well-rounded and Well-sorted sand grains indicate that sediment
Consider the following statements regarding Atmosphere.
- 99% of earth’s atmosphere is confined to the height of 320 km from earth’s surface.
- Hydrogen and Oxygen were the major constituents of early atmosphere.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
Continental shelf is formed due to:
- Rise in sea level
- Submergence of a part of a continent
- Sedimentary deposits brought down by rivers
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements.
- Maize requires moderate temperature, rainfall and lots of sunshine.
- Cotton requires high temperature, light rainfall, and less than hundred frost-free days and bright sunshine for its growth.
- Jute grows well on alluvial soil and requires high temperature, heavy rainfall and humid climate.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements.
- Deltas are formed in low tide regions, whereas Estuaries are formed in high tide region with rift valleys.
- Estuaries are usually more fertile than delta regions.
- Delta region continuously interacts with the ocean unlike estuaries which does not.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Cinnamomum camphora (from where Camphor can be obtained) is naturally found in
Consider the following statements:
- The enclosed seas in the low latitudes have lower temperature than the open seas.
- The enclosed seas in the high latitudes have higher temperature than the open seas
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding Ocean Currents.
- Ocean currents are not greatly influenced by coriolis force.
- The oceanic circulation pattern roughly corresponds to the earth’s atmospheric circulation pattern.
- In the southern hemisphere, the air circulation over the oceans in the middle latitudes is mainly cyclonic.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
Consider the following matches of specific disasters and related nodal agencies for early warning in the Government of India.
- Cyclone: Indian Meteorological Department
- Tsunami: Indian National Centre for Oceanic Information Services
- Floods: Central Water Commission
- Landslides: Geological Survey of India
Select the correct answer code:
Consider the following statements regarding ‘Drought Management in India’.
- There is no single, legally accepted definition of drought in India.
- Risk assessment and risk management of a drought falls within the purview of the Disaster Management Act, 2005.
- The Central government is the final authority to declare a region as drought affected.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
National Disaster Management Authority will involve in which of the following disasters?
- Urban Floods
- Heat Wave
- Nuclear and Radiological Disaster
- Chemical and Biological threat
Select the correct code:
Consider the following statements regarding State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF).
- SDRF was constituted based on the recommendations of the 14th Finance Commission.
- The Central Government contributes 50% to SDRF and the remaining 50% is provided from the State Government.
- A State Government may use the funds available under the SDRF for providing immediate relief to the victims of natural disasters that they consider to be ‘disasters’ within the local context in the State.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
Consider the following statements regarding National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF).
- NDRF is located in the “Public Accounts” of Government of India under “Reserve Funds not bearing interest”.
- The relief activities for all the calamities are monitored by the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- NDRF amount can be spent only towards meeting the expenses for emergency response, relief and rehabilitation.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
One can infer which of the following information from a population pyramid?
- Gender composition based on age groups
- Distribution of various age groups in a population
- Density of population
- Reproductive capabilities and likelihood of the continuation of a species
Select the correct answer code:
Consider the following statements.
- The fertility rate refers to the number of live births per 1000 women in the child-bearing age group, usually taken to be 15 to 49 years.
- Reaping demographic dividend due to a higher population of working-age citizens is usually the last stage in the demographic transition of any society.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
The term demographic trap is used by demographers to describe the combination of
- Sub-replacement level fertility rates
- High Fertility rate
- Declining mortality
- Increasing Mortality
Select the correct answer code:
The Census of India differentiates between urban and rural areas on which of the following criteria?
- Occupational structure
- Literacy rates
- Resource base
- Population size
Select the correct answer code:
Which of the following contribute to Monsoon breaks in India?
- When rain-bearing storms are not very frequent along the monsoon trough
- Over the west coast, when winds blow parallel to the coast.
- Tropical depressions during the south-west monsoon period
Select the correct answer code:
Consider the following statements.
- These soils are widespread in the northern plains and the river valleys.
- They are depositional soils, transported and deposited by rivers and streams.
- In the Peninsular region, they are found in deltas of the east coast.
The above statements refer to
High concentration of Teak and Sal forest are found in which topographic region
Consider the following statements:
- Roaring forties are the westerlies, lies between 40° and 50° latitude in Southern hemisphere.
- Horse latitudes are the low pressure and low temperature zone in 25-35 north and south latitude.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements.
- They are found in hills of the northeastern region and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- These forests are well stratified.
- Species found in these forests include rosewood, mahogany, aini and ebony.
The above statements refer to