Test: History - 14 - UPSC MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: History - 14
According to later vedic period, which of the following are correctly matched?
- Rajasuya – Chariot race
- Asvamedha – Horse sacrifice
- Vajpeya – Consecration ceremony
Select the correct answer code:
Consider the following statements regarding Rig Vedic Aryans.
- There are no evidences of the use of Iron by Rig Vedic Aryans.
- Trade was conducted on barter system.
- Gold coins called nishka were used as media of exchange in large transactions.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Consider the following statements regarding early vedic period.
- Only male gods like Prithvi, Agni, Vayu, Varuna, and Indra were worshipped.
- There were no temples and no idol worship during the early Vedic period.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements
- In the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War, the combined forces of the British East India Company and the Nizam of Hyderabad defeated Tipu Sultan.
- After Tipu Sultan was killed in the Battle of Seringapatam, Mysore was placed under Wodeyars – the former ruling dynasty.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Which of the following pairs is/are correctly matched?
- Lee Commission – Civil services
- Macdonnell commission – Public services
- Sargent plan – Education
- Aitchison commission – Press
Select the correct answer code:
Consider the following statements.
- Tashkent Declaration is a peace agreement between India and China signed after the Sino-IndianWar that occurred in 1962.
- Indus Water treaty is the only instance where India and Pakistan have allowed a third-party to help resolve their issues.
- Shimla Agreement, was signed between India and Pakistan following the Bangladesh Liberation war in 1971.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding Indo–Soviet Treaty of Peace, Friendship and Cooperation.
- Indo–Soviet Treaty of Peace, Friendship and Cooperation was a significant deviation from India’s previous position of non-alignment during the Cold War.
- The treaty played an important role in Sino-Indian War of 1962.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Bhoodan movement, a voluntary land reform movement in India, also advocated
- Gramdan (village in gift)
- Common ownership of land
Select the correct answer code:
Which of these are the core principles of Panchsheel?
- Non-Alignment
- Mutual non-aggression
- Neighbourhood First Policy
- Peaceful co- existing
- Equality and mutual benefit
Select the correct answer code:
Which of the following could be considered as the policy of the early days of the Non-Alignment Movement (NAM)?
- Not acting as a mediator to any bilateral or international conflict
- Staying away from joining any of the military alliances
- Staying out of wars
Select the correct answer code:
Which of the following regions were integrated by referendum in India?
- Hyderabad
- Junagarh
- Sikkim
- Nagaland
Select the correct answer code:
Consider the following statements.
- The first Five Year Plan was based on the ideas of Mahalanobis, which laid down the basic ideas regarding goals of Indian planning.
- The Second Five Year Plan tried to build the basis for a socialist pattern of society.
- In the first seven five-year plans, trade was characterised by import substitution strategy.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding Five Year Plans in India.
- The duration of plan holiday was from 1966 to 1969.
- “Garibi Hatao” slogan was given during Fourth Five Year Plan.
- Third Five Year Plan was based on the P.C. Mahalanobis Model.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding Mountbatten Plan
- Independence for princely states was ruled out in the Plan.
- Accession of Hyderabad to Pakistan.
- A boundary commission to be set up if partition was to be effected.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding the composition of Constituent assembly.
- The Constituent Assembly was constituted in November 1946 under the scheme formulated by the August offer.
- Constituent Assembly was a partly elected and partly nominated body.
- Seats were allotted on the basis of population at that time.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Which of the following historical commissions were related to States Reorganisation in India?
- JVP Committee
- Dhar Commission
- Fazl Ali Commission
- Gokhale Committee
Select the correct answer code:
Consider the following pairs.
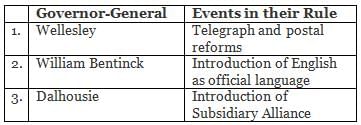
Which of the above pairs are correctly matched?
Consider the following statements
- Warren Hastings was the first to bring into existence and organise the civil services.
- Lytton introduced the statutory civil service.
- Satyendra Nath Tagore became the first Indian to qualify for the Indian Civil Service.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Aitchison Committee constituted during the British time is related to
Consider the following statements.
- The Cornwallis Code was a body of legislation enacted by the East India Company to improve the governance of its territories in India.
- The Permanent Settlement, which established a revenue collection scheme, was a part of the Cornwallis Code.
Which of the above is/are correct?
During his tenure, the Government of India Act, 1858 was passed which created the office of Viceroy to be held by the same person who was Governor General of India. He was

















