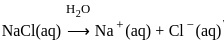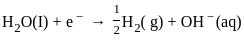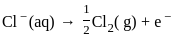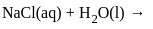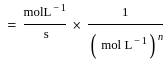Chemistry: CUET Mock Test - 2 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Chemistry: CUET Mock Test - 2
_________ is the basic repeated structural unit of a crystalline solid.
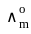 for NaCl, HCl and NaOAc are 126.4, 425.9 and 91.0 S cm2 mol-1 respectively. Calculate ∧° for HOAc
for NaCl, HCl and NaOAc are 126.4, 425.9 and 91.0 S cm2 mol-1 respectively. Calculate ∧° for HOAc
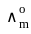 for NaCl, HCl and NaOAc are 126.4, 425.9 and 91.0 S cm2 mol-1 respectively. Calculate ∧° for HOAc
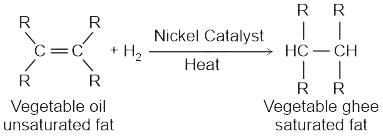
for NaCl, HCl and NaOAc are 126.4, 425.9 and 91.0 S cm2 mol-1 respectively. Calculate ∧° for HOAcWhich of the following catalysis is used in the hydrogenation of Vanaspati oil?
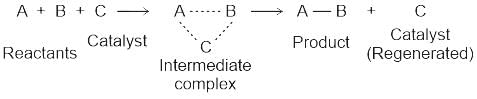
Which of the following statement is true regarding enzymes?
The rate constant of a reaction is 0.01s-1, how much time does it take for 2.4 mol L-1 concentration of reactant reduced to 0.3 mol L-1?
Sulfur exists in two polymorphic forms ________ and ________
When a single substance can crystallize in two or more forms under different conditions provided, it is called as _________
What time does it take for reactants to reduce to 3/4 of initial concentration if the rate constant is 7.5 x 10-3 s-1?
Which of the following is the correct expression for the temperature coefficient (n)?
Which of the following is not an example of lyophilic colloids?
What is the preferred electrode when it is not allowed to take part in the chemical reaction?
A zero-order reaction is 25% complete in 30seconds. What time does it take for 50% completion?
Solid-state is denser than the liquid and gaseous states of the same substance. Which of the following is an exception to this rule?
Which of the following is not an example of lyophobic colloids?
What is the product formed at the cathode in the electrolysis of molten NaCl?
What is the integrated rate equation for a first order reaction?
What happens to the peak of the curve in the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution graph if temperature increases?
In ______ constituent particles are closely packed leaving the least amount of vacant spaces.
What is the product formed at the cathode in the electrolysis of aqueous Na2SO4?
For a certain reaction the values of Arrhenius factor and Activation energy are 4 x 1013 collision/sec and 98.6KJ/mol at 303K. Calculate the rate constant if reaction is 1st order?( R = 8.341mol-1K-1)
Which of the following is the correct Arrhenius equation?
Which of the following is a characteristic of a multi-molecular colloid?


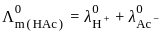
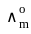 for NaCl, HCl and NaOAc are 126.4, 425.9 and 91.0 S cm2 mol-1
for NaCl, HCl and NaOAc are 126.4, 425.9 and 91.0 S cm2 mol-1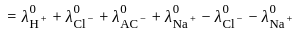
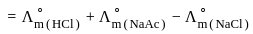

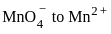 ?
?