Economics: CUET Mock Test - 4 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Economics: CUET Mock Test - 4
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. Capital-intensive production methods prioritize the use of labor over machinery.
ii. Choices made in production techniques can significantly affect the economy's overall efficiency.
iii. The problem of 'for whom to produce' focuses exclusively on personal income levels.
iv. An economy must decide not only what and how to produce but also how to distribute the produced goods.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. Scarcity leads to the need for economic choices among alternative uses of resources.
ii. The guiding principle of resource allocation is to maximize profit for producers.
iii. Civil goods and war goods must be chosen based on societal needs and available resources.
iv. The economic decision-making process is irrelevant to the satisfaction of consumer wants.
In a market economy, the central problems are solved by
An economy always produces on, but not inside a PPC.
Which of the following in an example of macro economics
Microeconomics is different from macroeconomic s as
Reserves arising from capital receipts are known as:
Which of the following statements about Globalisation is incorrect?
The market for sugar is in equilibrium. If the supply of sugar increases, the equilibrium price of sugar will ________ and the equilibrium quantity will _________.
The Industrial policy closely related to the trade Policy which aimed at replacing imports with domestic production is known as:
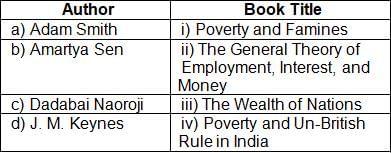
Match List-I with List-II :
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
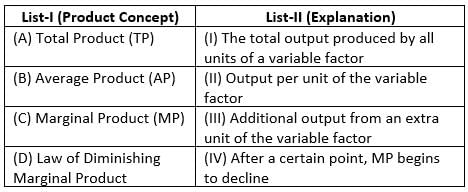
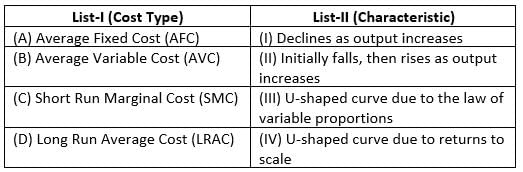
Match List-I with List-II :
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Generally, the value of currency of a country is expressed in terms of ________
Current account records all payments to rest of the world as ______ and all receipts from rest of the world as _____
Consider the following statements regarding
- Sen Index has been developed by Amartya sen.
- Sen Index is used to estimate poverty levels.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?