Psychology: CUET Mock Test - 1 - CUET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Psychology: CUET Mock Test - 1
Consider the following statements:
- Talent is a narrower term than giftedness.
- Intellectually gifted individuals show higher performance because of their outstanding potential.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
- Important decisions are taken by groups and not by individuals alone.
- Groups are more likely to take extreme decisions than individuals alone.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
- Emotional intelligence is a set of skills that underlie accurate appraisal, expression, and regulation of emotions.
- It helps to process emotional information accurately and efficiently.
Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect?
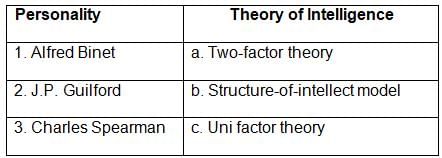
Match items of List I with List-II and then select the correct answer from the codes given below the lists.
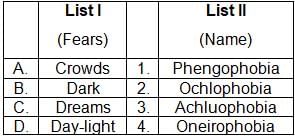
Match List I with List II
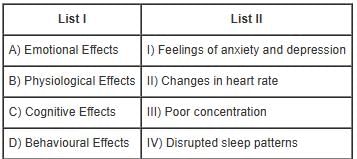
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
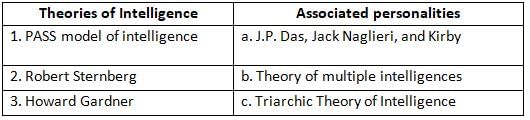
Match List I with List II
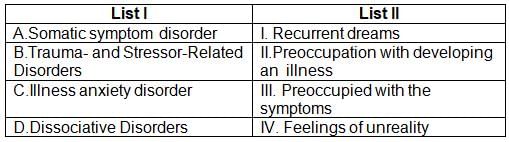
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Karim watches TV when he is stressed due to pending assignments in school. According to Endler and Parker, he is using _________ mechanism of coping.
_______ results from the blocking of needs and motives by something or someone that hinders us from achieving a desired goal.
__________ is the term used to describe the level of stress that is good for you.
"I should be loved by everyone at all times ", "I must be liked by all." This thought/belief can be treated using which therapy?
Total acceptance of the client and creating an environment wherein the client can freely express themselves is the modality used in ________ .
Many psychologists have stated that abnormal is simply a label that is given to a behaviour which is what?
What is removing the evil that resides in the individual through countermagic and prayer?
Who can an afflicted person learn which spirits are responsible for her/his problems?
In the 1957 Sidney Lumet film Twelve Angry Men, 12 jurors have to decide over the guilt or innocence of a young man charged with the murder of his father. At the outset, all but one of the jurors are convinced of the youth’s guilt. The lone juror (played by Henry Fonda) actively attempts to change their minds, standing firm, committed, self-confident and unwavering. One by one the other jurors change sides, until in the end they all agree that the accused is not guilty. Which form of social influence is this an example of?
Stroebe and Diehl (1994) conducted a clever piece of research into why brainstorming does not appear to enhance individual creativity. They hypothesized that, during a brainstorming session, because only one group member may speak at a time, other group members have to keep silent, and may be distracted by the content of the group discussion or forget their own ideas. Stroebe and Diehl termed this phenomenon ‘production blocking’, because the waiting time before speaking and the distracting influence of others’ ideas could potentially block individuals from coming up with their own ideas. The results of their subsequent study were clear-cut: participants generated approximately twice as many ideas when they were allowed to express their ideas as they occurred than when they had to wait their turn. But which TWO of the following can we infer from these results?
- That ‘production blocking’ does not occur in interactive brainstorming groups.
- That ‘production blocking’ is an important factor explaining the inferiority of interactive brainstorming groups.
- That it may be more effective to ask group members to develop their ideas in one group, and then express them to another group.
- That it may be more effective to ask group members to develop their ideas separately, and then express them in a subsequent joint meeting.
A person believes in helping others in need without expecting anything in return. This is an example of:
A negative attitude towards a particular group of people based on stereotypes is an example of:
An individual believes that people who wear glasses are intelligent. This is an example of:
Assertion (A): Attitudes are formed through a combination of personal experience, family, and social influences.
Reason (R): Attitudes are always inherited and not learned.
Who among the following psychologists divided all personalities into introverts and extroverts?
Which of the following is most widely used projective technique?
According to dynamic theorists, people use _____ to reduce their anxiety and guilt.
Anupam lacks patience, exhibits high motivation, feels burdened with work and always seems to be in a hurry. He needs to take care of himself as such people are prone to ailments like: