Biology: CUET Mock Test - 6 - Class 12 MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Biology: CUET Mock Test - 6
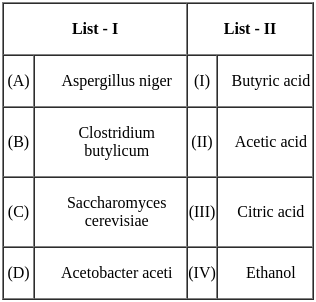
Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:

Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Identify the enzyme used for the isolation of genetic material from fungal cells.
Arrange the following steps of 'Polymerase Chain Reaction' in a correct sequence.
(A) Annealing of primers
(B) Amplified DNA
(C) Denaturation of DNA
(D) Extension of primers
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
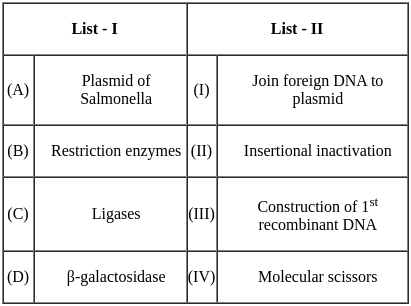
Match List - I with List - II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Without associating transiently with initiation - factor (σ) and termination - factor (ρ), the RNA polymerase is only capable of catalysing which of the following process ?
1. Initiation
2. Elongation
3. Termination
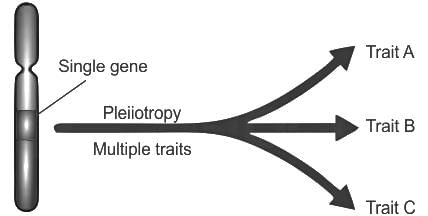
Consider the following statements.
1. Pleiotropy is the phenomenon of a single gene influencing two or more distinct phenotypic traits.
2. Phenylketonuria is a disease resulting from pleiotropy which is caused by a mutation of the gene.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
What are conditions having too much hydration called?
Who acts as a pioneering species in a xerarch succession?
In a xerarch succession, who secrete acids to dissolve rock?
Who replaces the shrub stage in a xerarch succession?
Xerarch succession is observed in which of the following area?
What will happen to biomass in an ecological succession from pioneer to climax community?
Which of the following is the correct sequence of xerarch succession?
In a plant succession, which is the last stabilized community?
Who replaces the herbaceous plants in a xerarch succession?
In a xerarch succession, who helps in weathering and soil formation?
What is the sequence of successional stages occurring on bare rocks called?
How many recombinant therapeutics have been approved for humans to date?
From which animals were insulin obtained in the early days?
The polypeptide chains present in insulin is connected by _______ bonds.