Test: Chemical Equilibrium: Law of Mass Action - NEET MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Chemical Equilibrium: Law of Mass Action
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-12) This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q.Conversion factor for converting partial pressures (in Kp) to active masses (in Kc) is
For which of the following reactions does the equilibrium constant depends on the unit of concentration?
The concentration of the oxides of nitrogen are monitored in air-pollution reports. At 25°C, the equilibrium constant for the reaction,
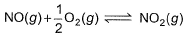
is 1.3 x 106 and that for
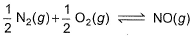
is 6.5 x 10-16 (when each species is expressed in terms of partial pressure).
For the reaction,
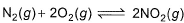
equilibrium constant is
is 1.3 x 106 and that for
is 6.5 x 10-16 (when each species is expressed in terms of partial pressure).
For the reaction,
equilibrium constant is
For the following gaseous phase equilibrium,
Kp is found to be equal to Kx (Kx is equilibrium constant when concentration are taken in terms of mole fraction. This is attained when pressure is
For the reaction in equilibrium, A B
Thus, K is
For the following equilibrium, N2O4 (g) 2NO2(g)
Kp = KC. This is attained when
is a gaseous phase equilibrium reaction taking place at 400 K in a 5 L flask. For this
A sample of pure PCI5(g)was introduced into an evacuated vessel at 473 K. After equilibrium was attained, concentration of PCI5 was found to be 0.05 mol L-1.
Thus, [PCI3] and [Cl2](in mol L-1)at equilibrium are
Ag+(aq)+NH3(aq) [Ag(NH3)(aq)]+ ; K, = 3.5x 10-3
[Ag(NH3)]+ (aq)+NH3(aq) [Ag(NH3)2]2+(aq); K2 = 1.7x 10-3
Formation constant of [Ag(NH3)2]+(aq) is
For the reversible reaction,
at 500° C, the value of Kp is 1.44x 10-5, when partial pressure is measured in atmosphere. The corresponding value of Kc with concentration in mol L-1 is
[IITJEE 2000]
For the reaction,
if Kp = Kc (RT)X, when the symbols have usual meaning, the value of x is (assuming ideality)
[jee Main 2014]
Given that for the equilibrium constants of two reactions,
areK1 and K2. Equilibrium constant k3 of the following reaction in terms of k1, and K2.
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-14) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
For the following type of reversible reaction,
Select the correct statement (s) about the following equilibrium.
Direction (Q. Nos. 15-18) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)
Passage I
At 573 K, PCI5 dissociates as,
PCI5 (g) ⇔ PCI3(g)+ Cl2 (g), Kp= 11.5 atm
Given, [PCI3]eq, = [Cl2]eq = 0.01 mol L-1
Q.
Kc of this equilibrium is
Passage II
The complex ion of Fe2+ with the chelating agent dipyridyl (abbreviated dipy) has been studied kinetically in both the forward and backward directions. For the complexion reaction,
the rate of the formation of the complex at 298 K is given by rate = (1. 45 x 1013 L3mol -3s-1) [Fe 2+] [dipy]3 and for the reverse reaction , the rate of disapperance of the complex is
Q. What is equilibrium constant for the equilibrium ?
Passage II
The complex ion of Fe2+ with the chelating agent dipyridyl (abbreviated dipy) has been studied kinetically in both the forward and backward directions. For the complexion reaction,
the rate of the formation of the complex at 298 K is given by rate = (1. 45 x 1013 L3mol -3s-1) [Fe 2+] [dipy]3 and for the reverse reaction , the rate of disapperance of the complex is
Q. If half-life Period of the backward reaction is (k = rate constant), then half-life period is about
Direction (Q. Nos. 19 and 20) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. At elevated temperature, PCl5 dissociates as,
At 300°C,Kp = 11.8 and
[PCI3]= [Cl2]= 0.01 moi L-1 at equilibrium.
[PCI5] = x x 10-4 mol L-1 what is the value of x?
What is Kp for the equation,
When the system contains equal number of Cl (g)atom and Cl2(g) molecules at 1 bar and 300 K?
Direction (Q. Nos. 21) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
The progress of the reaction with time t is shown below.
Match the parameters in Column l with their respective values in Column II.
Codes






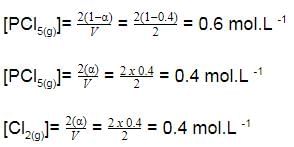
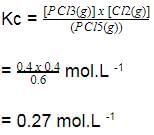


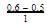 = 0.1
= 0.1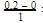 0.2
0.2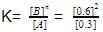 = 1.2mollitre−1
= 1.2mollitre−1