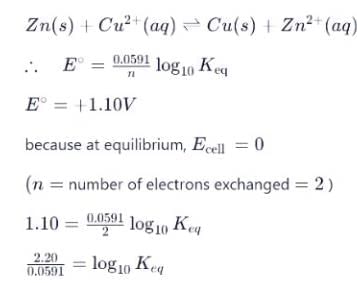Test: Thermodynamics of Chemical Equilibrium - JEE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Thermodynamics of Chemical Equilibrium
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-9) This section contains 9 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. For the reaction in equilibrium,
I. CO(g) + 1/2O2(g) 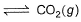
II. 2CO(g) + O2 (g) 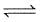 2CO2 (g)
2CO2 (g)

Then
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
I. CO(g) + 1/2O2(g)
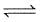 2CO2 (g)
2CO2 (g)Then
Equilibrium constant for the following equilibrium,
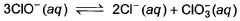
is 1.0 x 1028 at a temperature at which RT = 2500 J mol-1. Gibbs free energy change (ΔG°) is
is 1.0 x 1028 at a temperature at which RT = 2500 J mol-1. Gibbs free energy change (ΔG°) is
Kp for the equilibrium N2O4 (g) 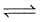 2NO2 (g) is 0.141 at 25°C and 1 bar. This reaction is spontaneous at 25°C and partial pressures of
2NO2 (g) is 0.141 at 25°C and 1 bar. This reaction is spontaneous at 25°C and partial pressures of
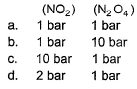
 2NO2 (g) is 0.141 at 25°C and 1 bar. This reaction is spontaneous at 25°C and partial pressures of
2NO2 (g) is 0.141 at 25°C and 1 bar. This reaction is spontaneous at 25°C and partial pressures ofFor the following equilibrium at 373 K,
H2O(g)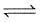 H2O(g)
H2O(g)
ΔAG° is
For the following electrochemical cell reaction at 298 K:
Zn(s) + Cu²⁺(aq) ⇌ Cu(s) + Zn²⁺(aq),
Given that the standard cell potential (E° cell) is +1.10 V.
Given
COCl2(g) 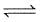 CO(g) + Cl2 (g)
CO(g) + Cl2 (g)
Kp = 8 x 10-9 atm
ΔS° = 30 cal K-1 at 373 K.
Temperature at which phosgene will be 0.1 % dissociated at 2 atm
(R = 2 cal mol-1K-1)is
For the following equilibrium at 298 K,
CO(g) + H2O (g) 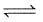 CO2(g) + H2(g);
CO2(g) + H2(g);
Δ f G° (in kcal mol-1) of CO = - 32.81, CO2 = - 94.26, H2O = - 54.64, H2 = 0.0 then, degree of dissociation of CO(g) is
At 1 atmospheric pressure, N2O4 is 50% dissociated at 300 K and 80% dissociated at 400 K as given
N2O4 (g) 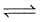 2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)
Thus, enthalpy of dissociation is
At 800 K, ΔG° for the reaction
NiO (s) + H2(g)  Ni (s) + H2O (g)
Ni (s) + H2O (g)
is - 9.0 kcal. Thus, ratio of pressures of water vapours and hydrogen in equilibrium with NiO and Ni at 800 K in terms of logarithm is
Direction (Q. Nos. 10) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.
Q. Statement I
For a reaction 2NO2(g)  N2O4 (g) variation of (log10 K) with (T-1) is represented as
N2O4 (g) variation of (log10 K) with (T-1) is represented as
Statement II
Association o f NO2 to N2O4 is an exotherm ic efiange.
Direction (Q. No. 11) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. Variation o f equilibrium constant K with tem perature, T is given by van’t Hoff equation
Graphically it is shown as given θ = tan (0 .5) and OP = 10
Thus,
Direction (Q. Nos. 12-13) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)
1 mole H2(g) and 0.2 mole CO2(g) are introduced in a vacuum flask at 450°C and 0.5 atm.
H2(g) + CO2  H2O(G) + CO(g)
H2O(G) + CO(g)
Analysis shows that mixture contains 10 moles per cent steam. Also equilibrium constant increases by one per cent per degree around 450°C.(log 1.1 = 0.0414)
Q. Equilibrium constant Kp is
1 mole H2(g) and 0.2 mole CO2(g) are introduced in a vacuum flask at 450°C and 0.5 atm.
H2(g) + CO2 (g)  H2O (g) + CO (g)
H2O (g) + CO (g)
Analysis shows that mixture contains 10 moles per cent steam. Also equilibrium constant increases by one per cent per degree around 450°C.(log 1.1 = 0.0414)
Q. ΔH (enthalpy change) by taking equilibrium constant at 450° C and 460° C is
Direction (Q. No. 14) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
The hydrogenation of pyridine (C5H5N) to piperidine (C5H11N)
C5H5N(g) + 3H2(g)  C5H11N(g)
C5H11N(g)
is an equilibrium process whose equilibrium constant (Kp)is given by
Match the thermodynamics parameters in column I with their respective values in column II.
Direction (Q. Nos. 15) This section contains 1 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
For a reversible reaction
Rate constant k1 (forward) = 1015e -2000/T and k2 (backward ) = 1012e -2000/T
What is the value of