Test: Kinetic Molecular Theory (Old NCERT) - JEE MCQ
19 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Kinetic Molecular Theory (Old NCERT)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-11) This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Helium atom is two times heavier than a hydrogen molecule (H2). At 298 K, the average kinetic energy of helium atom is
Mass of gas is 300 gm and its specific heat at constant volume is 750J/kg K. if gas is heated through 75°C at constant pressure of 105 N/m2, it expands by volume 0.08 × 106 cm3. find CP/CV.
At what temperature will the collision frequency in N2 be equal to that in He at 25°C if both gases are at a pressure of 1.00 bar collision diameter = 0.373 nm for N2 = 0.218 nm for He (Assume equal number of molecules per unit volume.)
According to the kinetic theory of gases, in an ideal gas, between two successive collisions a gas molecule travels
[IIT JEE 2003]
As the tem perature is raised from 20°C to 40°C. The average kinetic energy of the neon atoms changes by a factor of which of the following?
[IIT JEE 2004]
Which one of the following statements is not true about the effect of an increase in temperature on the distribution of molecular speeds in a gas?
[IIT JEE 2005]
Bond energy of H2 gas is 104 kcal mol-1. The temperature at which average kinetic energy of gaseous H2 molecules is equal to energy required to dissociate the molecules into atoms, is
Compressibility factor for CO2 at 400 K and 71.0 bar is 0.8697. Molar volume of CO2 under these conditions is
At what temperature will the hydrogen molecules have the same kinetic energy per mole as nitrogen molecules at 280 K?
Temperature at which average translation energy of a molecule is equal to the kinetic energy of the electron in first Bohr is orbit is
Pressure (p) of an ideal gas is related to kinetic energy (E) per unit volume by equation
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 and 13) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.
Q.
Statement I : The pressure exerted by a gas is the result of collisions of the molecules with the walls of the container.
Statement II : Due to collision, momentum is changed and rate of change of momentum is equal to force.
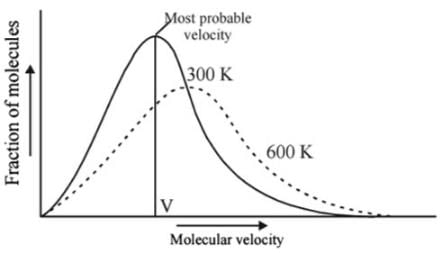
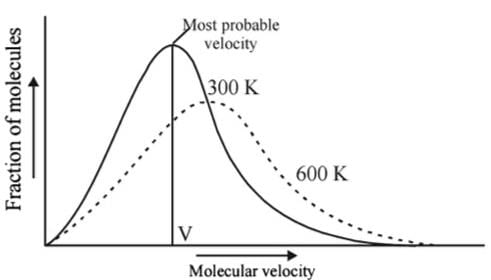
Statement I : As velocity increases, distribution of molecules increases and is maximum at most probable velocity, after which distribution of molecules decreases.
Statement II : Most probable velocity is given by
Direction (Q. Nos. 14-15) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. If a gas is expanded at constant temperature
According to kinetic theory of gases
[ITT JEE 2011]
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-19) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).
Passage I
Volume occupied by molecules is negligible compared to total volume of molecules. We have N2 gas molecules assuming them spherical of radius 200 pm.
Q.
Total volume of molecules contained in one mole of the gas is
Passage I
Volume occupied by molecules is negligible compared to total volume of molecules. We have N2 gas molecules assuming them spherical of radius 200 pm.
Q. Percentage of empty space available at STP is
Passage lI
Two flasks A and B have equal volumes as shown Both gases occupy 22.40 dm3 at STP. Also collision diameter of C2H4 molecule is four times than that of H2 molecule.
Q. In which flask and how many times are molecules moving faster?
Passage lI
Two flasks A and B have equal volumes as shown Both gases occupy 22.40 dm3 at STP. Also collision diameter of C2H4 molecule is four times than that of H2 molecule.
Q. In which flask and how many times is the mean free path of the molecules greater?