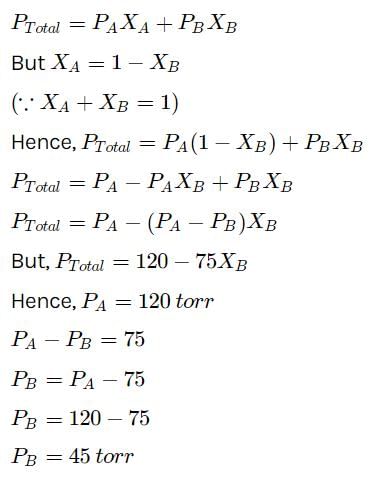Test: Vapour Pressure (Old NCERT) - JEE MCQ
18 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Vapour Pressure (Old NCERT)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-9) This section contains 9 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. A person living in Shimla observed that cooking of food without using pressure cooker takes more time. The reason for this observation is that at high altitude
Atmospheric pressures recorded in four metro cities are as follows :
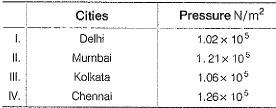
Q. Based on the above data, order in which water will boil (starting the earliest) in these cities is
At a given temperature, total vapour pressure (in torr) of a mixture of volatile components A and B is g iven by ptotal = 120 - 75 x B.
Hence, vapour pressure of pure A and B respectively are
Vapour pressure of mixture of 1 mole volatile liquid A and 1 mole volatile liquid B is 350 mm Hg at 50°C. On adding 2 moles of A Into mixture, vapour pressure increases by 25 mm Hg. Thus, vapour pressure of pure components are (in mm Hg)
Vapour pressure of a liquid is 380 mm Hg at 300 K and 570 mm Hg at 350 K. Thus, its normal boiling point is (log2 = 0.3010, log 1.5= 0.1761)
Heat of vaporisation of H2O is 40.6 kJ mol-1. At a 4000 m attitude , the atmospheric pressure is about 0.605 atm. What boiling point would you expect for water under these conditions?
Arrange ortho, meta and para-nitrophenols in increasing boiling points
A chemist decides to find the vapour pressure of water by the gas saturation method . 100 L of N2 gas is passed through 65.44 g of water. After passage of the gas, 63.13 g water remained. The temperature of water is 298 K.
Thus, vapour pressure of water is
Choose the correct statement with respect to the vapour pressure of a liquid among the following.
Direction (Q. Nos. 10-11) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
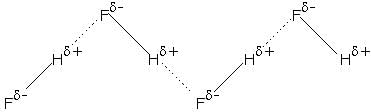
Q. HF molecule also exist in liquid state. Types of intermolecular forces between them a
Clausius-Clapeyron equation can be expressed as
Direction (Q. Nos. 12-15) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).
Passage I
For a given liquid at a given temperature vapour pressure is given by
Q. Thus, vapour pressure of the liquid at 400 K is
Passage I
For a given liquid at a given temperature vapour pressure is given by
Q. Latent heat of vaporisation in the given temperature range is
Passage II
Variation of log10 p with 1/T is given in the following graph (pressure in bar)
Q. Enthalpy of vaporisation based on this data is
Passage II
Variation of log10 p with 1/T is given in the following graph (pressure in bar)
Q. What is value of y, at point 1.0 x 10-2 K-1 on x-axis ?
Direction (Q. Nos. 15) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q. Variation of vapour pressure with temperature is given by
Graphically
Match the parameters in Column i with their values in Column II and select answer from codes given

Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. The vapour pressure of benzene C6H6 at 298 K is 95 torr. After 10.00 g of benzene is injected into a 10.0 L bulb at 298 K, how many grams of benzene remain as liquid?
113 L of helium gas at 1360°C and prevailing barometric pressure is passed through molten silver at 1360°C. The gas becomes saturated with silver vapour. As a result, the liquid silver loses 0.120 g in mass. What is the vapour pressure (in mm Hg) of liquid silver at 1360°C? Neglect any change in volume due to vaporisation of the silver.