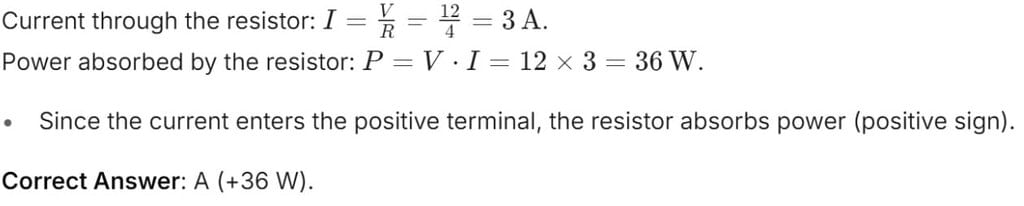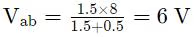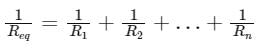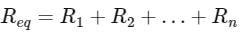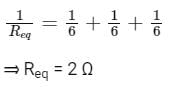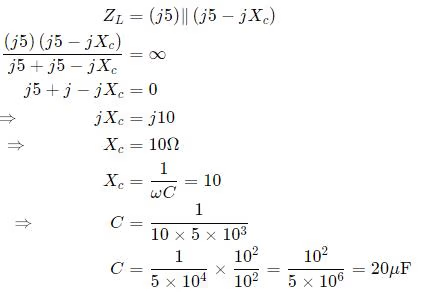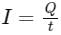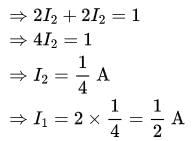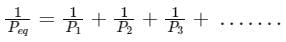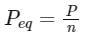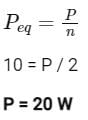Test: Network Elements - 1 - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Network Elements - 1
A resistor of 4 Ω is connected across a 12 V DC voltage source, with the current entering the positive terminal of the resistor. What is the power absorbed by the resistor?
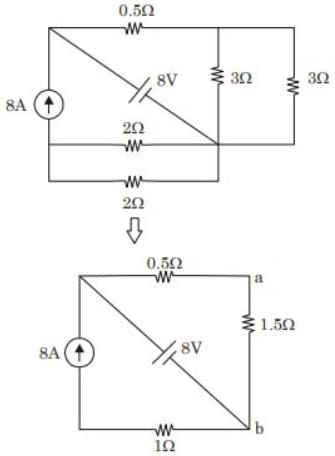
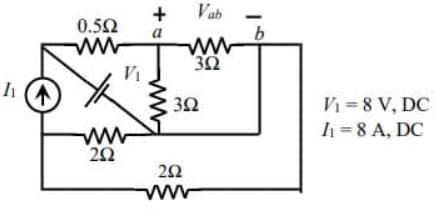
For the circuit shown in the figure, V1 =8 V, DC and I1 =8A, DC. The voltage Vab in Volts is ___ (Round off to 1 decimal place).

Three resistors of 6 Ω are connected in parallel. So, what will be the equivalent resistance?
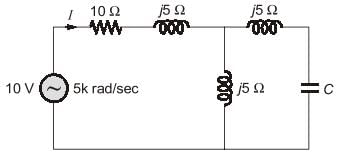
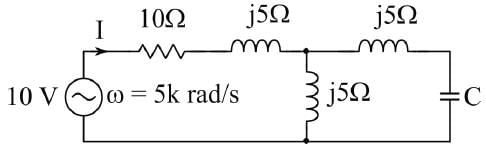
In the given circuit, the value of capacitor C that makes current I = 0 is __________μF.
If 5 A of electric current flows for a period of 3 minutes, what will be the amount of charge transferred?
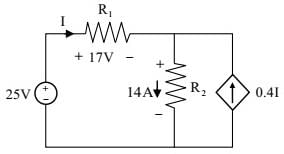
The power supplied by the 25 V source in the figure shown below is ________W.
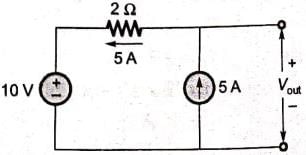
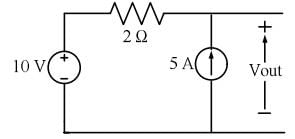
In the circuit shown below, the voltage and current sources are ideal. The voltage (Vout) across the current source, in volts, is
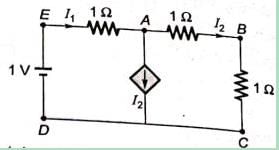
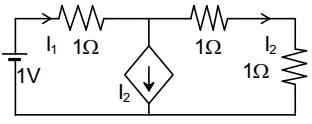
In the given circuit, the current supplied by the battery, in ampere, is _______.
When two identical resistors are connected in series across a battery, the power dissipated is 10 W. If these resistors are connected in parallel across the same battery, the total power dissipated will be
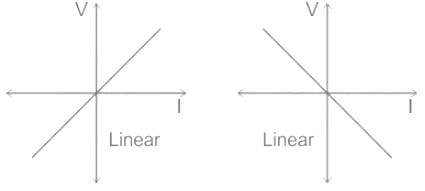
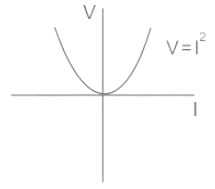
Consider an element represented by the relationship between current i (t) and voltage v (t) as follows: v(t) = i2(t). This device is classified as: