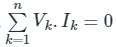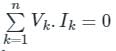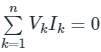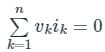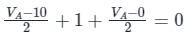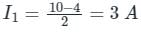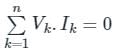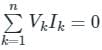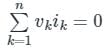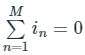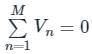Test: Tellegen's Theorem - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
9 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Tellegen's Theorem
According to Tellegen’s theorem, which one of the following is correct?
The total power developed in the circuit, if Vo = 125 V is
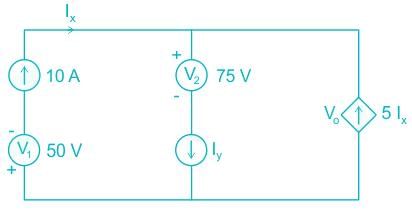

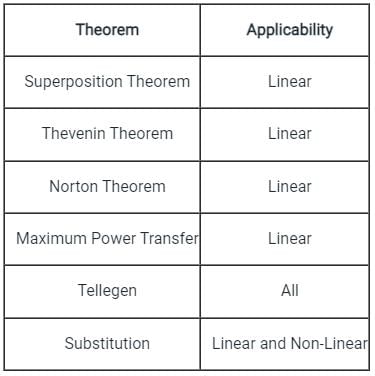
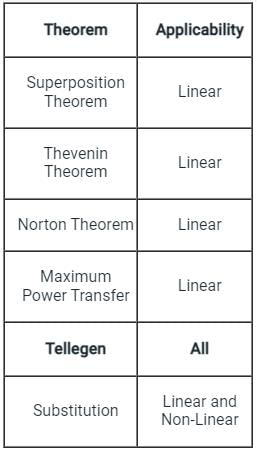
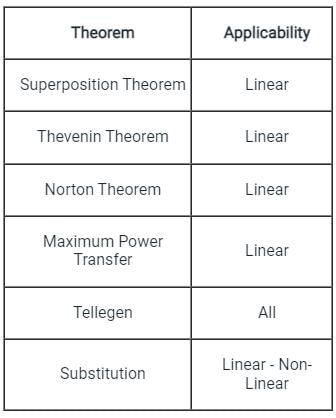
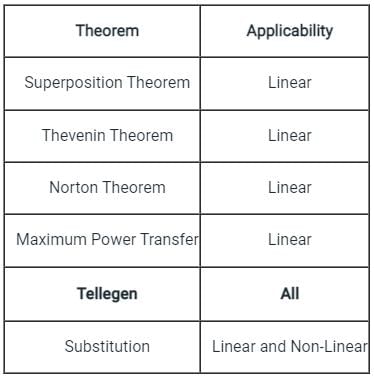
Which among the following theorems can be applied to any active or passive network?
Which of the following theorem can be applied to any network-linear or non-linear, active or passive, time-variant or time-invariant?
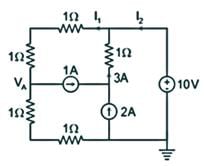
In the circuit shown below, the power supplied by the voltage source is?
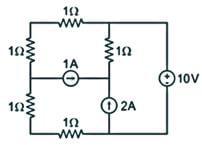
Which one of the following theorems is a manifestation of the Law of Conservation of Energy?
Tellegen’s theorem is based on the principle of law of __________.
The theorem which states that in any linear, non-linear, passive, active, time-variant and time-invariant network, the summation of instantaneous powers is zero will be called as