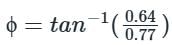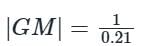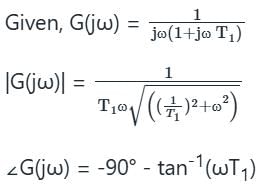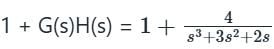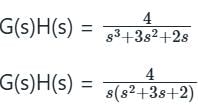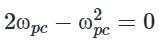Test: Polar Plot - 2 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Polar Plot - 2
The polar plot of the open loop transfer function of a feedback control system intersects the real axis at -2. The gain margin of the system is
The polar plot of a transfer function passes through the critical point (-1,0). Gain margin is
If the gain of the open-loop system is doubled, the gain margin
If a system has an open loop transfer function 1-s / 1+s, then the gain of the system at frequency of 1 rad/s will be
The gain margin for the system with open loop transfer function G(s) H(s) = G(s) = 2(1 + s) / s2 is
The open loop transfer function of a system is G(s) H(s) = K / (1 + s)(1 + 2s)(1 + 3s)
The phase cross over frequency ωc is
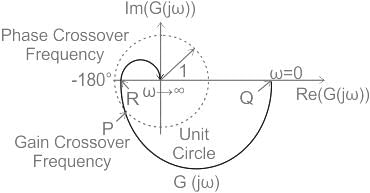
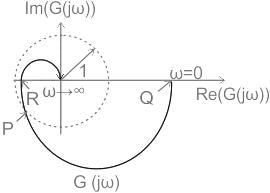
The Nyquist plot of a stable open-loop system G(jω) is plotted in the frequency range 0 ≤ ω < ∞ as shown. It is found to intersect a unit circle with center at the origin at the point �� = −0.77 − 0.64�� . The points �� and �� lie on G(jω) and assume values Q = 14.40 + 0.00j and R = −0.21 + 0.00j. The phase margin (PM) and the gain margin (GM) of the system are _____
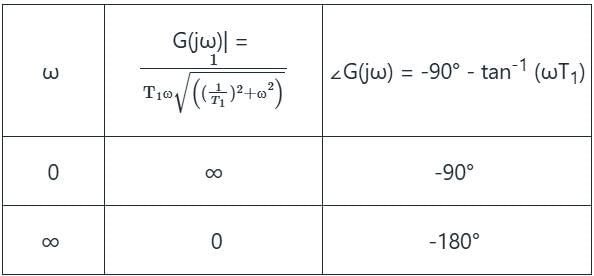
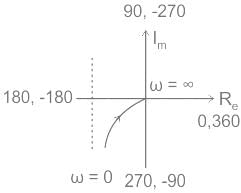
Obtain the polar plot for a system whose characteristic equation is
s3 + 3s2 + 2s + 4 = 0