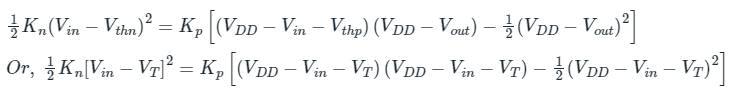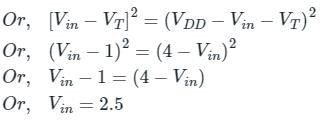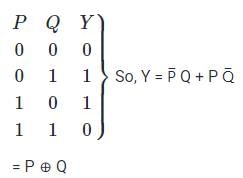Test: CMOS - 2 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: CMOS - 2
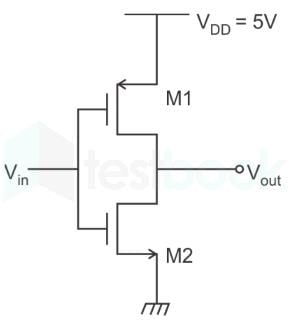
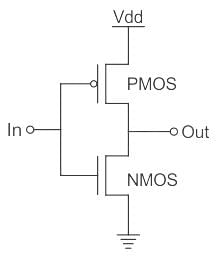
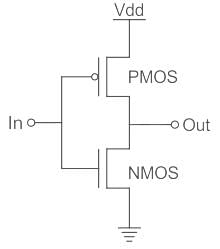
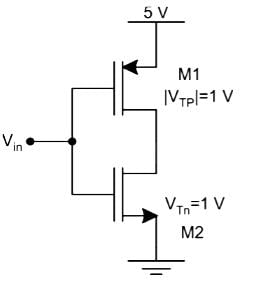
In the CMOS circuit shown, electron and hole mobilities are equal, and M1 and M2 are equally sized. The device M1 is in the linear region if

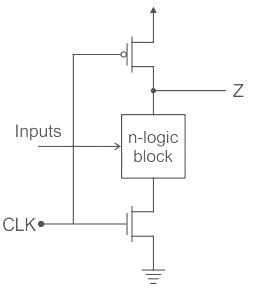
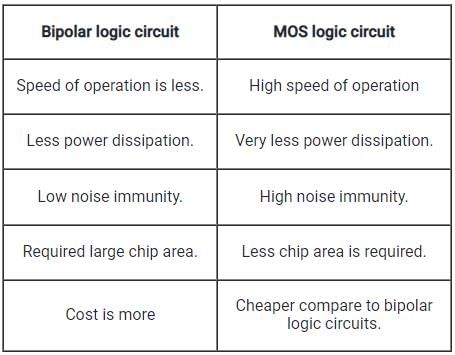
When there is no clock signal applied to CMOS logic circuits, they are referred to as
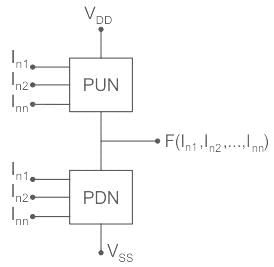
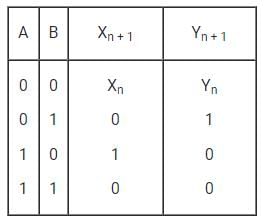
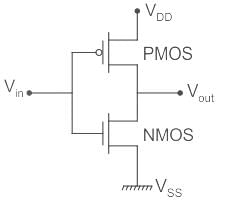
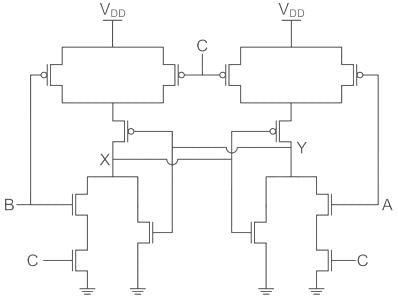
The following CMOS transistor based circuit with A, B, C as input and X, Y as output

A digital CMOS IC operating at 10 MHz clock frequency consumes 100 mW power; the same IC operating at 15 MHz clock frequency consumes 140mW power. What is the static power consumption of the IC?
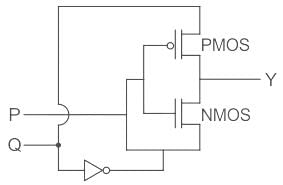
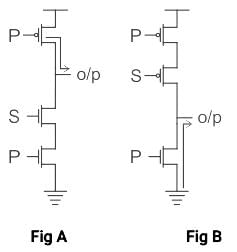
For the circuit shown in the figure, P and Q are the inputs and Y is the output.
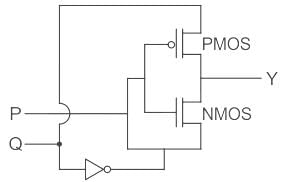
The logic implemented by the circuit is
For a typical CMOS process, the minimum feature size is set to be 25 μm. The minimum line width at the process is set to be ______
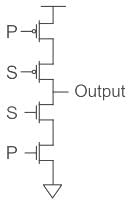
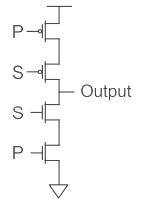
Output of the circuit shown below when S = 1 and S = 0 will be _____.